Robert Langer wins 2014 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences
Langer honored for his discoveries in controlled drug-release systems and new biomaterials; awards ceremony hosted by Kevin Spacey to be broadcast Jan. 27
New sensor tracks zinc in cells
Shifts in zinc’s location could be exploited for early diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Pills of the future: nanoparticles
Researchers design drug-carrying nanoparticles that can be taken orally
Creating synthetic antibodies
Synthetic polymers coating a nanoparticle surface can recognize specific molecules just like an antibody.
Catalyst for business
Startup Rive Technology is commercializing an MIT-developed invention that improves catalysts used in oil refining, leading to greater yields.
Self-steering particles go with the flow
Asymmetrical particles could make lab-on-a-chip diagnostic devices more efficient and portable.
Turning bacteria into chemical factories
Kristala Jones Prather engineers cells to produce useful compounds such as drugs and biofuels.
New implantable sensor paves way to long-term monitoring
Carbon nanotubes that detect nitric oxide can be implanted under the skin for more than a year.
One-two punch knocks out aggressive tumors
New nanoparticles weaken tumor-cell defenses, then strike with chemotherapy drug.
A pea-shooter for molecules
Researchers find that tiny molecules passing through nanotubes can be propelled or slowed depending on their size.
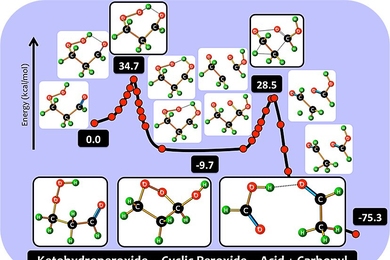
New low-temperature chemical reaction explained
Unusual reaction, never fully understood, is important to fuel combustion, atmospheric chemistry and biochemistry.
How to get fresh water out of thin air
Fog-harvesting system developed by MIT and Chilean researchers could provide potable water for the world’s driest regions.
Nanosensors could aid drug manufacturing
Chemical engineers find that arrays of carbon nanotubes can detect flaws in drugs and help improve production.