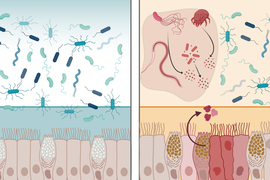
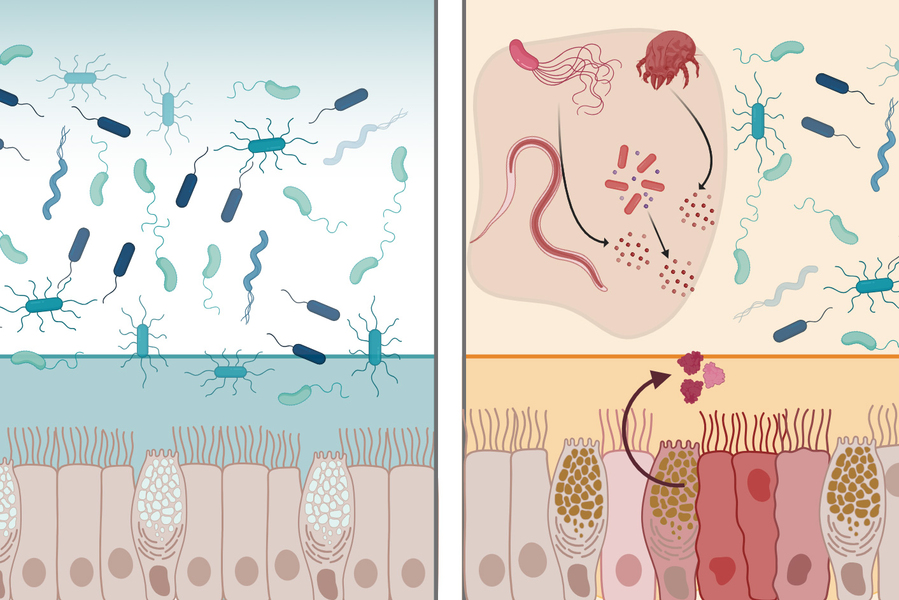
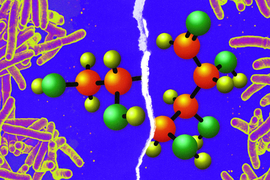
The mucosal surfaces that line the body are embedded with defensive molecules that help keep microbes from causing inflammation and infections. Among these molecules are lectins — proteins that recognize microbes and other cells by binding to sugars found on cell surfaces.
One of these lectins, MIT researchers have found, has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria found in the GI tract. This lectin, known as intelectin-2, binds to sugar molecules found on bacterial membranes, trapping the bacteria and hindering their growth. Additionally, it can crosslink molecules that make up mucus, helping to strengthen the mucus barrier.
“What’s remarkable is that intelectin-2 operates in two complementary ways. It helps stabilize the mucus layer, and if that barrier is compromised, it can directly neutralize or restrain bacteria that begin to escape,” says Laura Kiessling, the Novartis Professor of Chemistry at MIT and the senior author of the study.
This kind of broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity could make intelectin-2 useful as a potential therapeutic, the researchers say. It could also be harnessed to help strengthen the mucus barrier in patients with disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Amanda Dugan, a former MIT research scientist, and Deepsing Syangtan PhD ’24 are the lead authors of the paper, which appears today in Nature Communications.
A multifunctional protein
Current evidence suggests that the human genome encodes more than 200 lectins — carbohydrate-binding proteins that play a variety of roles in the immune system and in communication between cells. Kiessling’s lab, which has been exploring lectin-carbohydrate interactions, recently became interested in a family of lectins called intelectins. In humans, this family includes two lectins, intelectin-1 and intelectin-2.
Those two proteins have very similar structures, but intelectin-1 is distinctive in that it only binds to carbohydrates found in bacteria and other microbes. About 10 years ago, Kiessling and her colleagues were able to discover intelectin-1’s structure, but its functions are still not fully understood.
At that time, scientists hypothesized that intelectin-2 might play a role in immune defense, but there hadn’t been many studies to support that idea. Dugan, then a postdoc in Kiessling’s lab, set out to learn more about intelectin-2.
In humans, intelectin-2 is produced at steady levels by Paneth cells in the small intestine, but in mice, its expression from mucus-producing Goblet cells appears to be triggered by inflammation and certain types of parasitic infection.
In the new study, the researchers found that both human and mouse intelectin-2 bind to a sugar molecule called galactose. This sugar is commonly found in molecules called mucins that make up mucus. When intelectin-2 binds to these mucins, it helps to strengthen the mucus barrier, the researchers found.
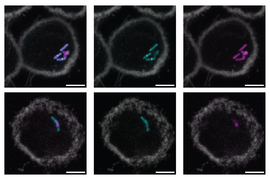
Galactose is also found in carbohydrates displayed on the surfaces of some bacterial cells. The researchers showed that intelectin-2 can bind to microbes that display these sugars, including many pathogens that cause GI infections.
The researchers also found that over time, these trapped microbes eventually disintegrate, suggesting that the protein is able to kill them by disrupting their cell membranes. This antimicrobial activity appears to affect a wide range of bacteria, including some that are resistant to traditional antibiotics.
These dual functions help to protect the lining of the GI tract from infection, the researchers believe.
“Intelectin-2 first reinforces the mucus barrier itself, and then if that barrier is breached, it can control the bacteria and restrict their growth,” Kiessling says.
Fighting off infection
In patients with inflammatory bowel disease, intelectin-2 levels can become abnormally high or low. Low levels could contribute to degradation of the mucus barrier, while high levels could kill off too many beneficial bacteria that normally live in the gut. Finding ways to restore the correct levels of intelectin-2 could be beneficial for those patients, the researchers say.
“Our findings show just how critical it is to stabilize the mucus barrier. Looking ahead, we can imagine exploiting lectin properties to design proteins that actively reinforce that protective layer,” Kiessling says.
Because intelectin-2 can neutralize or eliminate pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae, which are often difficult to treat with antibiotics, it could potentially be adapted as an antimicrobial agent.
“Harnessing human lectins as tools to combat antimicrobial resistance opens up a fundamentally new strategy that draws on our own innate immune defenses,” Kiessling says. “Taking advantage of proteins that the body already uses to protect itself against pathogens is compelling and a direction that we are pursuing.”
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health Glycoscience Common Fund, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the National Science Foundation.
Other authors who contributed to the study include Charles Bevins, a professor of medical microbiology and immunology at the University of California at Davis School of Medicine; Ramnik Xavier, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; and Katharina Ribbeck, the Andrew and Erna Viterbi Professor of Biological Engineering at MIT.