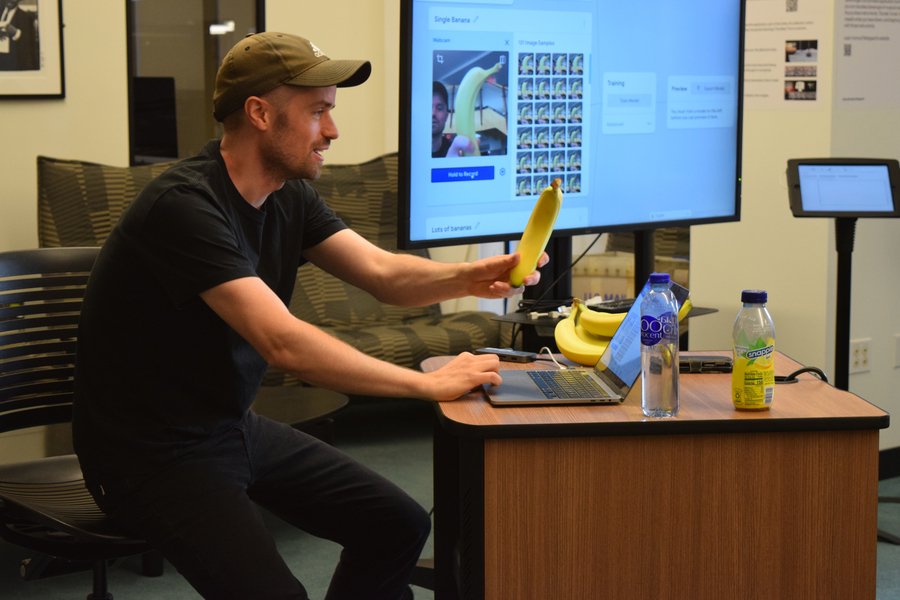
Sketch a doodle of a drum or a saxophone to conjure a multi-instrumental composition. Look into a webcam, speak, and watch your mouth go bouncing across the screen — the input for a series of charmingly clunky chain reactions.
This is what visitors to the MIT Lewis Music Library encounter when they interact with two new digital installations, “Doodle Tunes” and “Sounds from the Mouth,” created by 2022-23 Center for Art and Technology (CAST) Visiting Artist Andreas Refsgaard in collaboration with Music Technology and Digital Media Librarian Caleb Hall. The residency was initiated by Avery Boddie, Lewis Music Library department head, who recognized Refsgaard’s flair for revealing the playfulness of emerging technologies. The intricacies of coding and machine learning can seem daunting to newcomers, but Refsgaard’s practice as a creative coder, interaction designer, and educator seeks to open the field to all. Encompassing workshops, an artist talk, class visits, and an exhibition, the residency was infused with his unique sense of humor — a combination of lively eccentricity and easygoing relatability.
Learning through laughter
Refsgaard, who is based in Copenhagen, is a true maverick of machine learning. “I’m interested in the ways we can express ourselves through code,” he explains. “I like to make unconventional connections between inputs and outputs, with the computer serving as a translator — a tool might allow you to play music with your eyes, or it might generate a love poem from a photo of a burrito.” Refsgaard’s particular spin on innovation isn’t about directly solving problems or launching world-changing startups. Instead, he simply seeks to “poke at what can be done,” providing accessible open-source templates to prompt new creative ideas and applications.
Programmed by Refsgaard and featuring a custom set of sounds created by Hall, “Doodle Tunes” and “Sounds from the Mouth” demonstrate how original compositions can be generated through a mix of spontaneous human gestures and algorithmically produced outputs. In “Doodle Tunes,” a machine learning algorithm is trained on a dataset of drawings of different instruments: a piano, drums, bass guitar, or saxophone. When the user sketches one of these images on a touchscreen, a sound is generated; the more instruments you add, the more complex the composition. “Sounds from the Mouth” works through facial tracking and self-capturing images. When the participant faces a webcam and opens their mouth, an autonomous snapshot is created which bounces off the notes of a piano. To try the projects for yourself, scroll to the end of this article.
Libraries, unlimited
Saxophone squeals and digital drum beats aren’t the only sounds issuing from the areas where the projects are installed. “My office is close by,” says Hall. “So when I suddenly hear laughter, I know exactly what’s up.” This new sonic dimension of the Lewis Music Library fits with the ethos of the environment as a whole — designed as a campus hub for audio experimentation, the library was never intended to be wholly silent. Refsgaard’s residency exemplifies a new emphasis on progressive programming spearheaded by Boddie, as the strategy of the library shifts toward a focus on digital collections and music technology.
“In addition to serving as a space for quiet study and access to physical resources, we want the library to be a place where users congregate, collaborate, and explore together,” says Boddie. “This residency was very successful in that regard. Through the workshops, we were able to connect individuals from across the MIT community and their unique disciplines. We had people from the Sloan School of Management, from the Schwarzman College of Computing, from Music and Theater Arts, all working together, getting messy, creating tools that sometimes worked … and sometimes didn’t.”
Error and serendipity
The integration of error is a key quality of Refgaard’s work. Occasional glitches are part of the artistry, and they also serve to gently undermine the hype around AI; an algorithm is only as good as its dataset, and that set is inflected by human biases and oversights. During a public artist talk, “Machine Learning and the Arts,” audience members were initiated into Refsgaard’s offbeat artistic paradigm, presented with projects such as Booksby.ai (an online bookstore for AI-produced sci-fi novels), Is it FUNKY? (an attempt to distinguish between “fun” and “boring” images), and Eye Conductor (an interface to play music via eye movements and facial gestures). Glitches in the exhibit installations were frankly admitted (it’s true that “Doodle Tunes” occasionally mistakes a drawing of a saxophone for a squirrel), and Refsgaard encouraged audience members to suggest potential improvements.
This open-minded attitude set the tone of the workshops “Art, Algorithms and Artificial Intelligence” and “Machine Learning for Interaction Designers,” intended to be suitable for newcomers as well as curious experts. Refsgaard’s visits to music technology classes explored the ways that human creativity could be amplified by machine learning, and how to navigate the sliding scale between artistic intention and unexpected outcomes. “As I see it, success is when participants engage with the material and come up with new ideas. The first step of learning is to understand what is being taught — the next is to apply that understanding in ways that the teacher couldn’t have foreseen.”
Uncertainty and opportunity
Refsgaard’s work exemplifies some of the core values and questions central to the evolution of MIT Libraries — issues of digitization, computation, and open access. By choosing to make his lighthearted demos freely accessible, he renounces ownership of his ideas; a machine learning model might serve as a learning device for a student, and it might equally be monetized by a corporation. For Refsgaard, play is a way of engaging with the ethical implications of emerging technologies, and Hall found himself grappling with these questions in the process of creating the sounds for the two installations. “If I wrote the sound samples, but someone else arranged them as a composition, then who owns the music? Or does the AI own the music? It’s an incredibly interesting time to be working in music technology; we’re entering into unknown territory.”
For Refsgaard, uncertainty is the secret sauce of his algorithmic artistry. “I like to make things where I’m surprised by the end result,” he says. “I’m seeking that sweet spot between something familiar and something unexpected.” As he explains, too much surprise simply amounts to noise, but there’s something joyful in the possibility that a machine might mistake a saxophone for a squirrel. The task of a creative coder is to continually tune the relationship between human and machine capabilities — to find and follow the music.
“Doodle Tunes” and “Sounds from the Mouth” are on display in the MIT Lewis Music Library (14E-109) until Dec. 20. Click the links to interact with the projects online.