Computer science meets economics
Constantinos Daskalakis adapts techniques from theoretical computer science to game theory.
A virtual “guide dog” for navigation
Low-power chip processes 3-D camera data, could enable wearable device to guide the visually impaired.
Recognizing correct code
Automatic bug-repair system fixes 10 times as many errors as its predecessors.
Computer science and engineering major helps people while having fun
Senior Sami Alsheikh helps others, solves problems, and has fun doing both.
Mapping regulatory elements
Systematically searching DNA for regulatory elements indicates limits of previous thinking.
Switchable material could enable new memory chips
Small voltage can flip thin film between two crystal states — one metallic, one semiconducting.
Drones dodge obstacles
Motion-planning algorithms allow drones to do donuts, figure-eights in object-filled environments.
Cutting down runway queues
Model that predicts time from gate departure to takeoff could cut airport congestion, fuel waste.
Smarter driving, using your phone
App that rates drivers’ behavior yields promising safety results on the road.
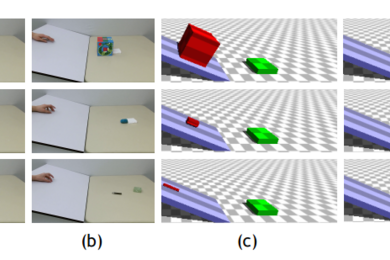
Computer model matches humans at predicting how objects move
“3-D physics engine” from the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory simulates the human brain to infer physical properties.
Optoelectronic microprocessors built using existing chip manufacturing
High-performance prototype means chipmakers could now start building optoelectronic chips.
Machines that learn like people
Algorithms could learn to recognize objects from a few examples, not millions; may better model human cognition.
MIT Lincoln Laboratory receives three 2015 R&D 100 Awards
Three software products named among 100 most technologically significant innovations of 2015.
Detecting consumer decisions within messy data
Software analyzes online chatter to predict health care consumers’ behavior.