Search Stories
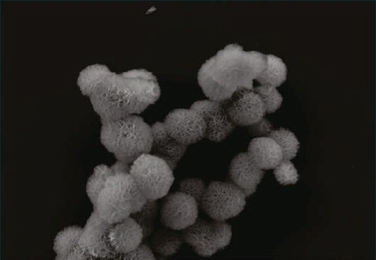
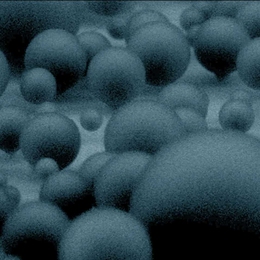
Delivering RNA with tiny sponge-like spheres
New RNA interference method holds promise for treating cancer, other diseases.
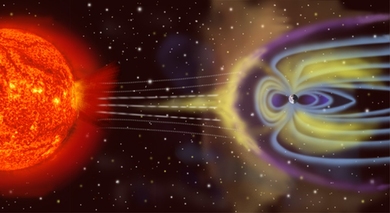
Mysterious electron acceleration explained
Computer simulation identifies source of aurora-causing high-speed electrons in space
When (and where) work disappears
Study: Overseas manufacturing competition hits U.S. regions hard, leaving workers unemployed for years and local economies struggling.
Knight Fellows offer tips on tackling the energy and climate science beat
Science journalists discuss the current state of their profession and its future.
Unique languages, universal patterns
MIT linguist reveals how modern English resembles Old Japanese, and other surprising convergences between far-flung tongues.
Making droplets drop faster
New nanopatterned surfaces could improve the efficiency of powerplants and desalination systems.
3 Questions: Adam Berinsky on the unpredictable GOP campaign
Political scientist who studies public opinion assesses a campaign with wildly fluctuating polls.
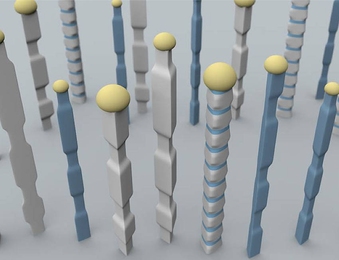
A new twist on nanowires
Technology developed at MIT can control the composition and structure of these tiny wires as they grow.
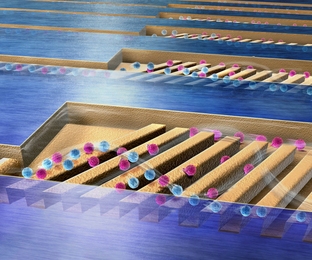
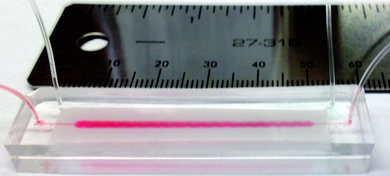
A faster way to catch cells
New microfluidic device could be used to diagnose and monitor cancer and other diseases.
Toying with biological systems
By swapping microbial genes, Chris Voigt designs cells with novel functions.
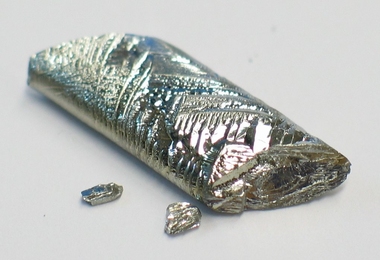
An element that's rare on Earth is found far, far away
Tellurium detected for the first time in ancient stars.
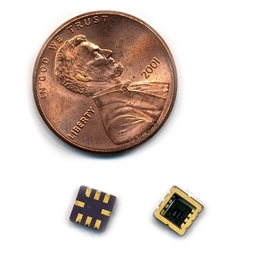
Successful human tests for first wirelessly controlled drug-delivery chip
Clinical trial of the programmable, implantable device shows promise in treating osteoporosis.