MIT Professor Emeritus Barry Lloyd Vercoe, a pioneering force in computer music, a founding faculty member of the MIT Media Lab, and a leader in the development of MIT’s Music and Theater Arts Section, passed away on June 15. He was 87.
Vercoe’s life was a rich symphony of artistry, science, and innovation that led to profound enhancements of musical experience for expert musicians as well as for the general public — and especially young people.
Born in Wellington, New Zealand, on July 24, 1937, Vercoe earned bachelor’s degrees in music (in 1959) and mathematics (in 1962) from the University of Auckland, followed by a doctor of musical arts in music composition from the University of Michigan in 1968.
After completing postdoctoral research in digital audio processing at Princeton University and a visiting lectureship at Yale University, Vercoe joined MIT’s Department of Humanities (Music) in 1971, beginning a tenure in the department that lasted through 1984. During this period, he played a key role in advancing what would become MIT’s Music and Theater Arts (MTA) Section, helping to shape its forward-thinking curriculum and interdisciplinary philosophy. Vercoe championed the integration of musical creativity with scientific inquiry, laying the groundwork for MTA’s enduring emphasis on music technology and experimental composition.
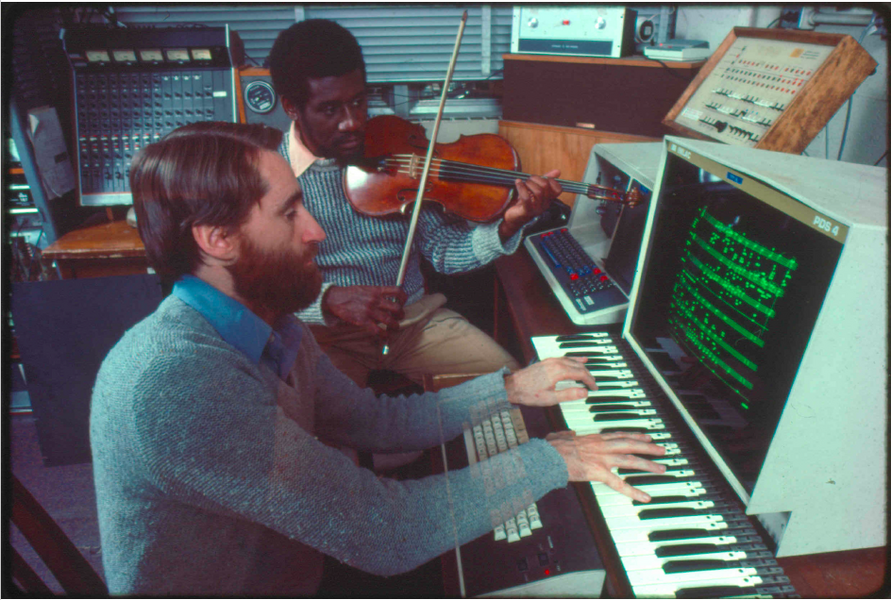
In 1973, Vercoe founded MIT’s Experimental Music Studio (EMS) — the Institute’s first dedicated computer music facility, and one of the first in the world. Operated under the auspices of the music program, EMS became a crucible for innovation in algorithmic composition, digital synthesis, and computer-assisted performance. His leadership not only positioned MIT as a hub for music technology, but also influenced how the Institute approached the intersection of the arts with engineering. This legacy is honored today by a commemorative plaque in the Kendall Square MBTA station.
Violist, faculty founder of the MIT Chamber Music Society, and Institute Professor Marcus Thompson says: “Barry was first and foremost a fine musician, and composer for traditional instruments and ensembles. As a young professor, he taught our MIT undergraduates to write and sing Renaissance counterpoint as he envisioned how the act of traditional music-making offered a guide to potential artistic interaction between humans and computers. In 1976, he enlisted me to premiere what became his iconic, and my most-performed, work, ‘Synapse for Viola and Computer.’”
During a Guggenheim Fellowship in 1982–83, Vercoe developed the Synthetic Performer, a groundbreaking real-time interactive accompaniment system, while working closely with flautist Larry Beauregard at the Institute for Research and Coordination in Acoustics/Music (IRCAM) in Paris.
In 1984, Vercoe became a founding faculty member of the MIT Media Lab, where he launched the Music, Mind, and Machine group. His research spanned machine listening, music cognition, and real-time digital audio synthesis. His Csound language, created in 1985, is still widely used for music programming, and his contributions helped define the MPEG-4 Structured Audio standard.
He also served as associate academic head of the Media Lab’s graduate program in Media Arts and Sciences (MAS). Vercoe mentored many future leaders in digital music and sound computation, including two of his MAS graduate students — Anna Huang SM ’08 and Paris Smaragdis PhD ’01 — who have recently joined MIT’s music faculty, and Miller Puckette, an emeritus faculty member at the University of California at San Diego, and Richard Boulanger, a professor of electronic production and design at the Berklee College of Music.
“Barry Vercoe will be remembered by designers, developers, researchers, and composers for his greatest ‘composition,’ Csound, his free and open-source software synthesis language,” states Boulanger. “I know that, through Csound, Barry’s musical spirit will live on, not only in my teaching, my research, and my music, but in the apps, plugins, and musical compositions of generations to come.”
Tod Machover, faculty director of the MIT Media Lab and Muriel R. Cooper Professor of Music and Media, reflects, “Barry Vercoe was a giant in the field of computer music whose innovations in software synthesis, interactive performance, and educational tools for young people influenced and inspired many, including myself. He was a superb mentor, always making sure that artistic sensibility drove music tech innovation, and that sophisticated expression was at the core of Media Lab — and MIT — culture.”
Vercoe’s work earned numerous accolades. In addition to the Guggenheim Fellowship, he was also honored with the 1992 Computerworld Smithsonian Award for innovation and the 2004 SEAMUS Lifetime Achievement Award.
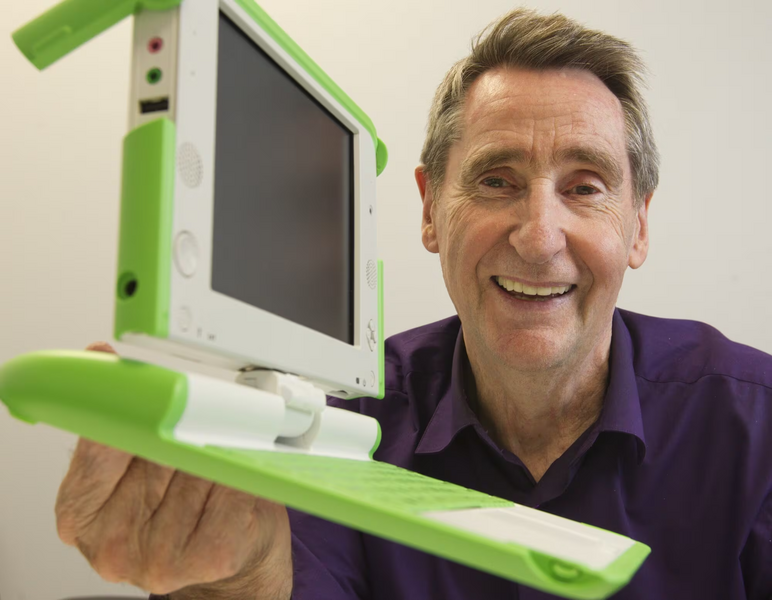
Beyond MIT, Vercoe consulted with Analog Devices and collaborated with international institutions like IRCAM under the direction of Pierre Boulez. His commitment to democratizing music technology was evident in his contributions to the One Laptop per Child initiative, which brought accessible digital sound tools to young people in underserved communities worldwide.
He is survived by his former wives, Kathryn Veda Vaughn and Elizabeth Vercoe; their children, Andrea Vercoe and Scott Vercoe; and generations of students and collaborators who continue to build on his groundbreaking work. A memorial service for family will be held in New Zealand later this summer, and a special event in his honor will take place at MIT in the fall. The Media Lab will share details about the MIT gathering as they become available.
Named professor emeritus at the MIT Media Lab upon his retirement in 2010, Vercoe’s legacy embodies the lab’s — and MIT’s — vision of creative, ethical, interdisciplinary research at the convergence of art, science, and technology. His music, machines, and generously inventive spirit will continue to forever shape the way we listen, learn, and communicate.