To achieve the aspirational goal of the Paris Agreement on climate change — limiting the increase in global average surface temperature to 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels — will require its 196 signatories to dramatically reduce their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Those greenhouse gases differ widely in their global warming potential (GWP), or ability to absorb radiative energy and thereby warm the Earth’s surface. For example, measured over a 100-year period, the GWP of methane is about 28 times that of carbon dioxide (CO2), and the GWP of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is 24,300 times that of CO2, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Sixth Assessment Report.
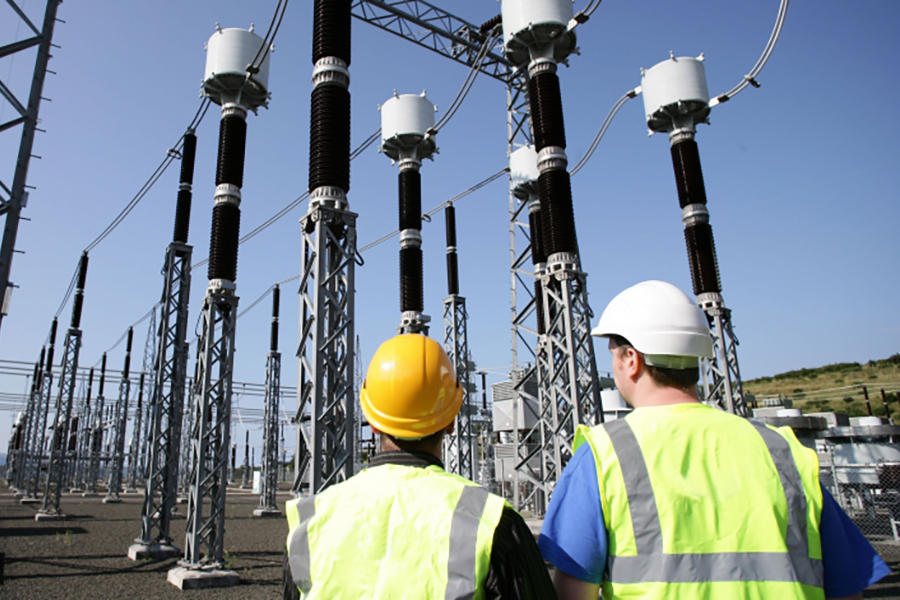
Used primarily in high-voltage electrical switchgear in electric power grids, SF6 is one of the most potent greenhouse gases on Earth. In the 21st century, atmospheric concentrations of SF6 have risen sharply along with global electric power demand, threatening the world’s efforts to stabilize the climate. This heightened demand for electric power is particularly pronounced in China, which has dominated the expansion of the global power industry in the past decade. Quantifying China’s contribution to global SF6 emissions — and pinpointing its sources in the country — could lead that nation to implement new measures to reduce them, and thereby reduce, if not eliminate, an impediment to the Paris Agreement’s aspirational goal.
To that end, a new study by researchers at the MIT Joint Program on the Science and Policy of Global Change, Fudan University, Peking University, University of Bristol, and Meteorological Observation Center of China Meteorological Administration determined total SF6 emissions in China over 2011-21 from atmospheric observations collected from nine stations within a Chinese network, including one station from the Advanced Global Atmospheric Gases Experiment (AGAGE) network. For comparison, global total emissions were determined from five globally distributed, relatively unpolluted “background” AGAGE stations, involving additional researchers from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and CSIRO, Australia's National Science Agency.
The researchers found that SF6 emissions in China almost doubled from 2.6 gigagrams (Gg) per year in 2011, when they accounted for 34 percent of global SF6 emissions, to 5.1 Gg per year in 2021, when they accounted for 57 percent of global total SF6 emissions. This increase from China over the 10-year period — some of it emerging from the country’s less-populated western regions — was larger than the global total SF6 emissions rise, highlighting the importance of lowering SF6 emissions from China in the future.
The open-access study, which appears in the journal Nature Communications, explores prospects for future SF6 emissions reduction in China.
“Adopting maintenance practices that minimize SF6 leakage rates or using SF6-free equipment or SF6 substitutes in the electric power grid will benefit greenhouse-gas mitigation in China,” says Minde An, a postdoc at the MIT Center for Global Change Science (CGCS) and the study’s lead author. “We see our findings as a first step in quantifying the problem and identifying how it can be addressed.”
Emissions of SF6 are expected to last more than 1,000 years in the atmosphere, raising the stakes for policymakers in China and around the world.
“Any increase in SF6 emissions this century will effectively alter our planet’s radiative budget — the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy from the Earth — far beyond the multi-decadal time frame of current climate policies,” says MIT Joint Program and CGCS Director Ronald Prinn, a coauthor of the study. “So it’s imperative that China and all other nations take immediate action to reduce, and ultimately eliminate, their SF6 emissions.”
The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China and Shanghai B&R Joint Laboratory Project, the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and other funding agencies.