Faculty highlight: Christopher Schuh
Metallurgist pushes grain boundaries: Nanostructured metal alloys deliver tougher materials, lower costs, and safer outcomes.
Microscopic “walkers” find their way across cell surfaces
Technology could provide a way to deliver probes or drugs to cell structures without outside guidance.
Solid nanoparticles can deform like a liquid
Unexpected finding shows tiny particles keep their internal crystal structure while flexing like droplets.
Nanoparticles get a magnetic handle
New method produces particles that can glow with color-coded light and be manipulated with magnets.
Unconventional photoconduction in an atomically thin semiconductor
New mechanism of photoconduction could lead to next-generation excitonic devices.
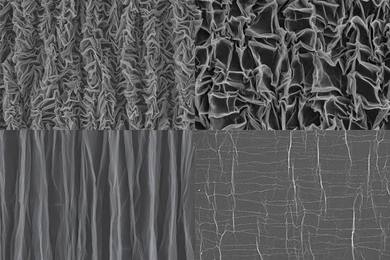
Crumpled graphene could provide an unconventional energy storage
Two-dimensional carbon “paper” can form stretchable supercapacitors to power flexible electronic devices.
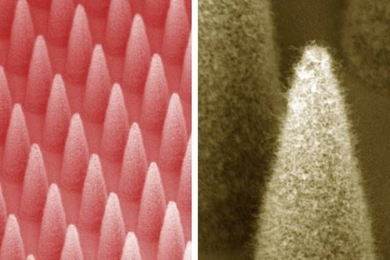
Fast, cheap nanomanufacturing
Arrays of tiny conical tips that eject ionized materials could fabricate nanoscale devices cheaply.
Faculty highlight: Michael Rubner
Materials scientist Mike Rubner’s collaboration with chemical engineer Robert Cohen yields anti-fog coatings, synthetic "backpacks" for living cells.
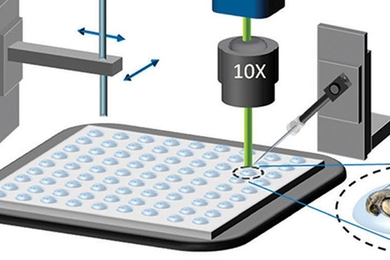
High-speed biologics screen
Engineers devise technology for rapidly testing drug-delivery vehicles in zebrafish.
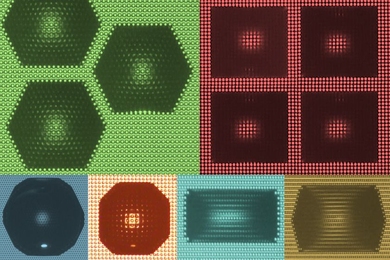
How to make a “perfect” solar absorber
New system aims to harness the full spectrum of available solar radiation.
Magnetic neural control with nanoparticles
Customized arrays of iron oxide nanoparticles are possible based on their differing responses to alternating magnetic fields, MIT researchers report.
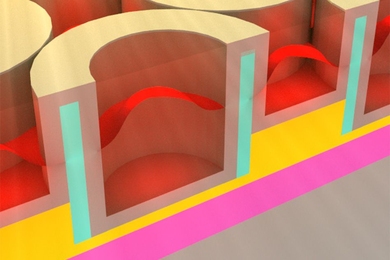
Toward optical chips
A promising light source for optoelectronic chips can be tuned to different frequencies.