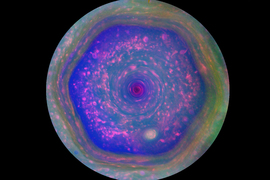
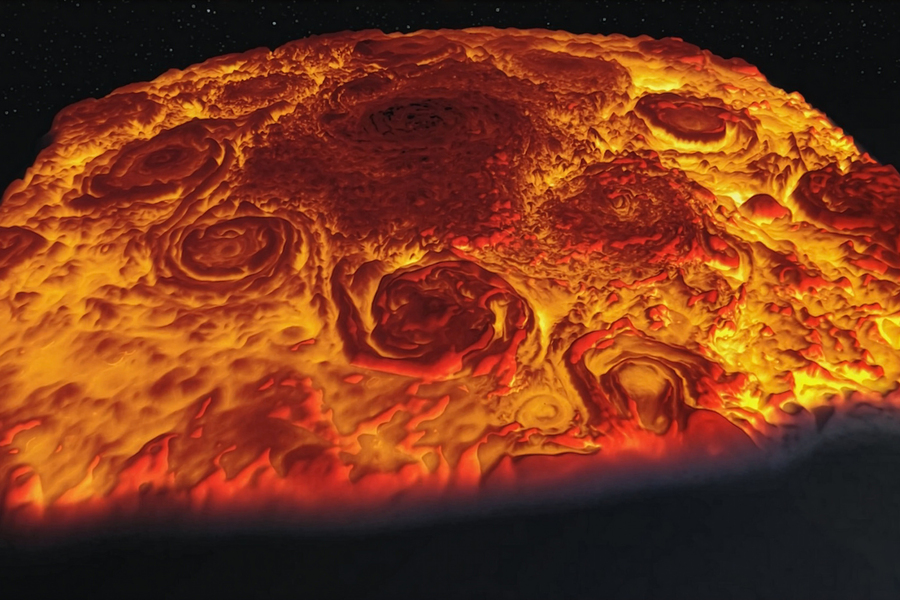
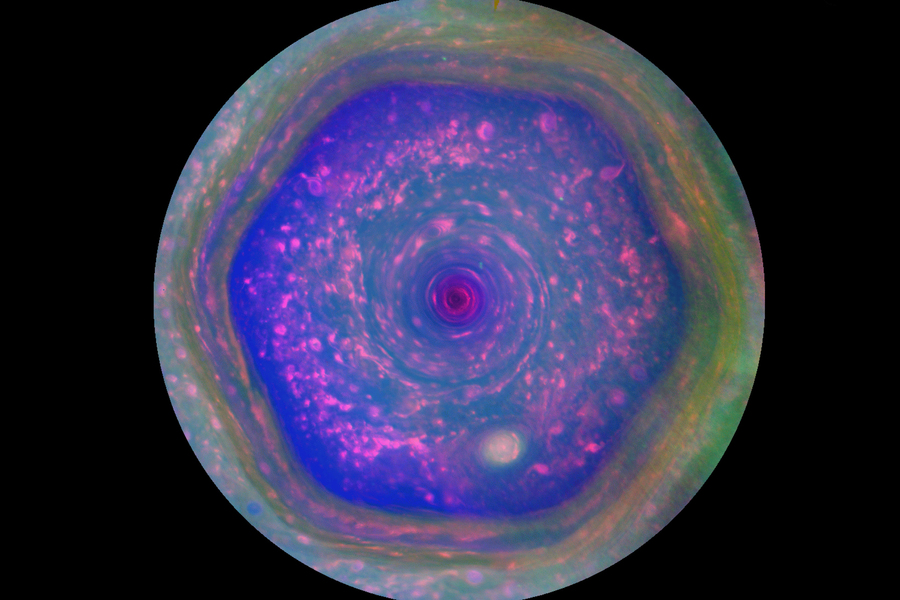
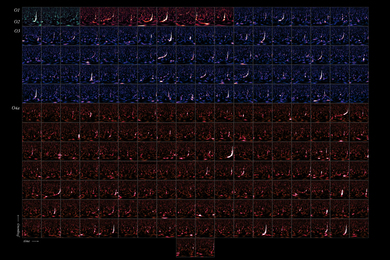
Over the years, passing spacecraft have observed mystifying weather patterns at the poles of Jupiter and Saturn. The two planets host very different types of polar vortices, which are huge atmospheric whirlpools that rotate over a planet’s polar region. On Saturn, a single massive polar vortex appears to cap the north pole in a curiously hexagonal shape, while on Jupiter, a central polar vortex is surrounded by eight smaller vortices, like a pan of swirling cinnamon rolls.
Given that both planets are similar in many ways — they are roughly the same size and made from the same gaseous elements — the stark difference in their polar weather patterns has been a longstanding mystery.
Now, MIT scientists have identified a possible explanation for how the two different systems may have evolved. Their findings could help scientists understand not only the planets’ surface weather patterns, but also what might lie beneath the clouds, deep within their interiors.
In a study appearing this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team simulates various ways in which well-organized vortex patterns may form out of random stimulations on a gas giant. A gas giant is a large planet that is made mostly of gaseous elements, such as Jupiter and Saturn. Among a wide range of plausible planetary configurations, the team found that, in some cases, the currents coalesced into a single large vortex, similar to Saturn’s pattern, whereas other simulations produced multiple large circulations, akin to Jupiter’s vortices.
After comparing simulations, the team found that vortex patterns, and whether a planet develops one or multiple polar vortices, comes down to one main property: the “softness” of a vortex’s base, which is related to the interior composition. The scientists liken an individual vortex to a whirling cylinder spinning through a planet’s many atmospheric layers. When the base of this swirling cylinder is made of softer, lighter materials, any vortex that evolves can only grow so large. The final pattern can then allow for multiple smaller vortices, similar to those on Jupiter. In contrast, if a vortex’s base is made of harder, denser stuff, it can grow much larger and subsequently engulf other vortices to form one single, massive vortex, akin to the monster cyclone on Saturn.
“Our study shows that, depending on the interior properties and the softness of the bottom of the vortex, this will influence the kind of fluid pattern you observe at the surface,” says study author Wanying Kang, assistant professor in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS). “I don’t think anyone’s made this connection between the surface fluid pattern and the interior properties of these planets. One possible scenario could be that Saturn has a harder bottom than Jupiter.”
The study’s first author is MIT graduate student Jiaru Shi.
Spinning up
Kang and Shi’s new work was inspired by images of Jupiter and Saturn that have been taken by the Juno and Cassini missions. NASA’s Juno spacecraft has been orbiting around Jupiter since 2016, and has captured stunning images of the planet’s north pole and its multiple swirling vortices. From these images, scientists have estimated that each of Jupiter’s vortices is immense, spanning about 3,000 miles across — almost half as wide as the Earth itself.
The Cassini spacecraft, prior to intentionally burning up in Saturn’s atmosphere in 2017, orbited the ringed planet for 13 years. Its observations of Saturn’s north pole recorded a single, hexagonal-shaped polar vortex, about 18,000 miles wide.
“People have spent a lot of time deciphering the differences between Jupiter and Saturn,” Shi says. “The planets are about the same size and are both made mostly of hydrogen and helium. It’s unclear why their polar vortices are so different.”
Shi and Kang set out to identify a physical mechanism that would explain why one planet might evolve a single vortex, while the other hosts multiple vortices. To do so, they worked with a two-dimensional model of surface fluid dynamics. While a polar vortex is three-dimensional in nature, the team reasoned that they could accurately represent vortex evolution in two dimensions, as the fast rotation of Jupiter and Saturn enforces uniform motion along the rotating axis.
“In a fast-rotating system, fluid motion tends to be uniform along the rotating axis,” Kang explains. “So, we were motivated by this idea that we can reduce a 3D dynamical problem to a 2D problem because the fluid pattern does not change in 3D. This makes the problem hundreds of times faster and cheaper to simulate and study.”
Getting to the bottom
Following this reasoning, the team developed a two-dimensional model of vortex evolution on a gas giant, based on an existing equation that describes how swirling fluid evolves over time.
“This equation has been used in many contexts, including to model midlatitude cyclones on Earth,” Kang says. “We adapted the equation to the polar regions of Jupiter and Saturn.”
The team applied their two-dimensional model to simulate how fluid would evolve over time on a gas giant under different scenarios. In each scenario, the team varied the planet’s size, its rate of rotation, its internal heating, and the softness or hardness of the rotating fluid, among other parameters. They then set a random “noise” condition, in which fluid initially flowed in random patterns across the planet’s surface. Finally, they observed how the fluid evolved over time given the scenario’s specific conditions.
Over multiple different simulations, they observed that some scenarios evolved to form a single large polar vortex, like Saturn, whereas others formed multiple smaller vortices, like Jupiter. After analyzing the combinations of parameters and variables in each scenario and how they related to the final outcome, they landed on a single mechanism to explain whether a single or multiple vortices evolve: As random fluid motions start to coalesce into individual vortices, the size to which a vortex can grow is limited by how soft the bottom of the vortex is. The softer, or lighter the gas is that is rotating at the bottom of a vortex, the smaller the vortex is in the end, allowing for multiple smaller-scale vortices to coexist at a planet’s pole, similar to those on Jupiter.

Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
Conversely, the harder or denser a vortex bottom is, the larger the system can grow, to a size where eventually it can follow the planet’s curvature as a single, planetary-scale vortex, like the one on Saturn.
If this mechanism is indeed what is at play on both gas giants, it would suggest that Jupiter could be made of softer, lighter material, while Saturn may harbor heavier stuff in its interior.
“What we see from the surface, the fluid pattern on Jupiter and Saturn, may tell us something about the interior, like how soft the bottom is,” Shi says. “And that is important because maybe beneath Saturn’s surface, the interior is more metal-enriched and has more condensable material which allows it to provide stronger stratification than Jupiter. ”
"Because Jupiter and Saturn are otherwise so similar, their different polar weather has been a puzzle,” says Yohai Kaspi, a professor of geophysical fluid dynamics at the Weizmann Institute of Science, and a member of the Juno mission’s science team, who was not involved in the new study. “The work by Shi and Kang reveals a surprising link between these differences and the planets’ deep interior ‘softness’, offering a new way to map the key internal properties that shape their atmospheres."
This research was supported, in part, by a Mathworks Fellowship and endowed funding from MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences.