For Chen Chu MArch ’21, the invitation to join the 2023-24 cohort of Morningside Academy for Design Design Fellows has been an unparalleled opportunity to investigate the potential of design as an alternative method of problem-solving.
After earning a master’s degree in architecture at MIT and gaining professional experience as a researcher at an environmental nongovernmental organization, Chu decided to pursue a PhD in the Department of Urban Studies and Planning. “I discovered that I needed to engage in a deeper way with the most difficult ethical challenges of our time, especially those arising from the fact of climate change,” he explains. “For me, MIT has always represented this wonderful place where people are inherently intellectually curious — it’s a very rewarding community to be part of.”
Chu’s PhD research, guided by his doctoral advisor Delia Wendel, assistant professor of urban studies and international development, focuses on how traditional practices of floodplain agriculture can inform local and global strategies for sustainable food production and distribution in response to climate change.
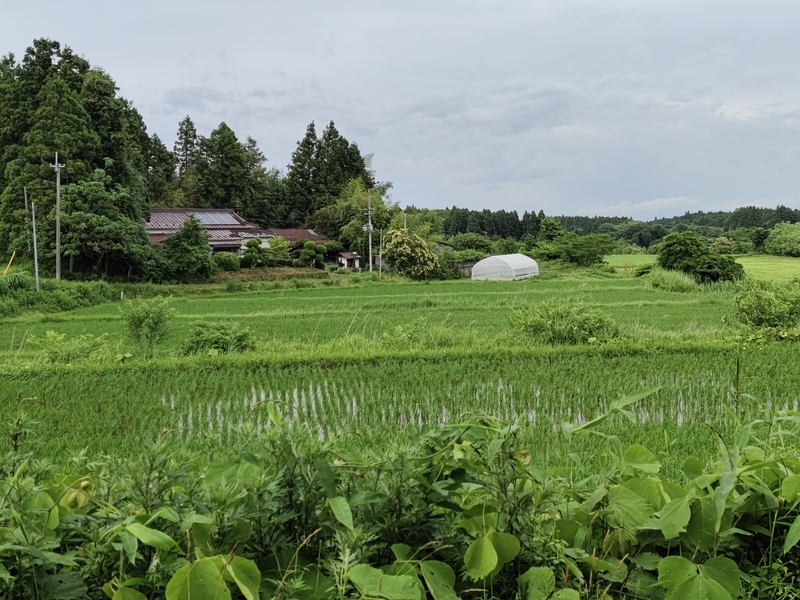
Typically located alongside a river or stream, floodplains arise from seasonal flooding patterns that distribute nutrient-rich silt and create connectivity between species. This results in exceptionally high levels of biodiversity and microbial richness, generating the ideal conditions for agriculture. It’s no accident that the first human civilizations were founded on floodplains, including Mesopotamia (named for its location poised between two rivers, the Euphrates and Tigris), the Indus River Civilization, and the cultures of Ancient Egypt based around the Nile. Riverine transportation networks and predictable flooding rhythms provide a framework for trade and cultivation; nonetheless, floodplain communities must learn to live with risk, subject to the sudden disruptions of high waters, drought, and ecological disequilibrium.
For Chu, the “unstable and ungovernable” status of floodplains makes them fertile ground for thinking about. “I’m drawn to these so-called ‘wet landscapes’ — edge conditions that act as transitional spaces between land and water, between humans and nature, between city and river,” he reflects. “The development of extensively irrigated agricultural sites is typically a collective effort, which raises intriguing questions about how communities establish social organizations that simultaneously negotiate top-down state control and adapt to the uncertainty of nature.”
Chu is in the process of honing the focus of his dissertation and refining his data collection methods, which will include archival research and fieldwork, as well as interviews with floodplain inhabitants to gain an understanding of sociopolitical nuances. Meanwhile, his role as a design fellow gives him the space to address the big questions that fire his imagination. How can we live well on shared land? How can we take responsibility for the lives of future generations? What types of political structures are required to get everyone on board?
These are just a few of the questions that Chu recently put to his cohort in a presentation. During the weekly seminars for the fellowship, he has the chance to converse with peers and mentors of multiple disciplines — from researchers rethinking the pedagogy of design to entrepreneurs applying design thinking to new business models to architects and engineers developing new habitats to heal our relationship with the natural world.
“I’ll admit — I’m wary of the human instinct to problem-solve,” says Chu. “When it comes to the material conditions and lived experience of people and planet, there’s a limit to our economic and political reasoning, and to conventional architectural practice. That said, I do believe that the mindset of a designer can open up new ways of thinking. At its core, design is an interdisciplinary practice based on the understanding that a problem can’t be solved from a narrow, singular perspective.”
The stimulating structure of a MAD Fellowship — free from immediate obligations to publish or produce, fellows learn from one another and engage with visiting speakers via regular seminars and events — has prompted Chu to consider what truly makes for generative conversation in the contexts of academia and the private and public sectors. In his opinion, discussions around climate change often fail to take account of one important voice; an absence he describes as “that silent being, the Earth.”
“You can’t ask the Earth, ‘What does justice mean to you?’ Nature will not respond,” he reflects. To bridge the gap, Chu believes it’s important to combine the study of specific political and social conditions with broader existential questions raised by the environmental humanities. His own research draws upon the perspectives of thinkers including Dipesh Chakrabarty, Donna Haraway, Peter Singer, Anna Tsing, and Michael Watts, among others. He cites James C. Scott’s lecture “In Praise of Floods” as one of his most important influences.
In addition to his instinctive appreciation for theory, Chu’s outlook is grounded by an attention to innovation at the local level. He is currently establishing the parameters of his research, examining case studies of agricultural systems and flood mitigation strategies that have been sustained for centuries.
“One example is the polder system that is practiced in the Netherlands, China, Bangladesh, and many parts of the world: small, low-lying tracts of land submerged in water and surrounded by dykes and canals,” he explains. “You’ll find a different but comparable strategy in the colder regions of Japan. Crops are protected from the winter winds by constructing a spatial unit with the house at the center; trees behind the house serve as windbreakers and paddy fields for rice are located in front of the house, providing an integrated system of food and livelihood security.”
Chu observes that there is a tendency for international policymakers to overlook local solutions in favor of grander visions and ambitious climate pledges — but he is equally keen not to romanticize vernacular practices. “Realistically, it's always a two-way interaction. Unless you already have a workable local system in place, it’s difficult to implement a solution without top-down support. On the other hand, the large-scale technocratic dreams are empty if ignorant of local traditions and histories.”
By navigating between the global and the local, the theoretical and the practical, the visionary and the cautionary, Chu has hope in the possibility of gradually finding a way toward long-term solutions that adapt to specific conditions over time. It’s a model of ambition and criticality that Chu sees played out during dialogue at MAD and within his department; at root, he’s aware that the outcome of these conversations depends on the ethical context that shapes them.
“I've been fortunate to have many mentors who have taught me the power of humility; a respect for the finitude, fragility, and uncertainty of life,” he recalls. “It’s a mindset that’s barely apparent in today’s push for economic growth.” The flip-side of hubristic growth is an assumption that technological ingenuity will be enough to solve the climate crisis, but Chu’s optimism arises from a different source: “When I feel overwhelmed by the weight of the problems we’re facing, I just need to look around me,” he says. “Here on campus — at MAD, in my home department, and increasingly among the new generations of students — there’s a powerful ethos of political sensitivity, ethical compassion, and an attention to clear and critical judgment. That always gives me hope for the planet.”