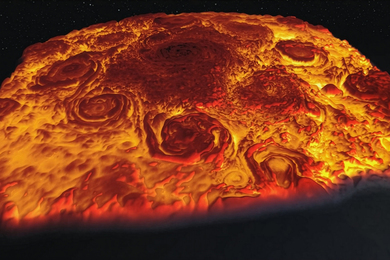
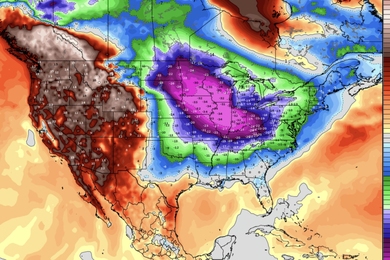
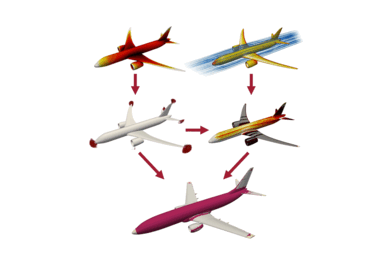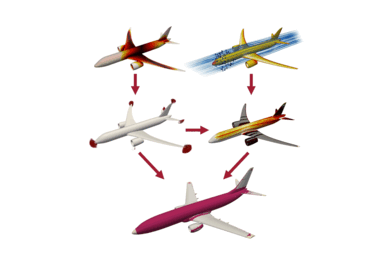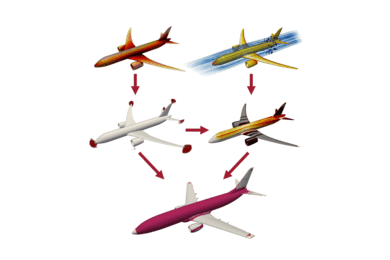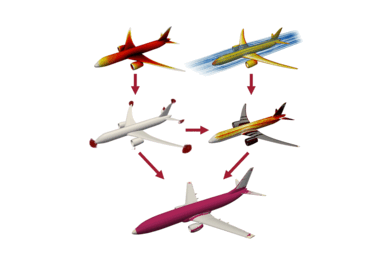
Featured video: How tiny satellites help us track hurricanes and other weather events
Mini microwave sounders developed at Lincoln Laboratory, demonstrated on a NASA mission, and now transferred to industry, are expanding storm-forecasting capabilities.