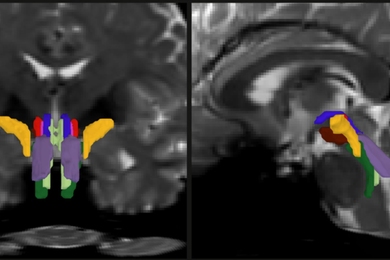
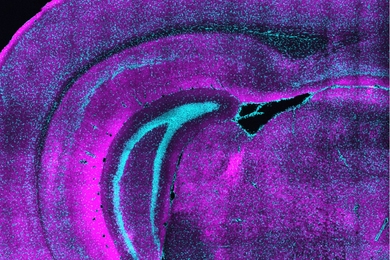
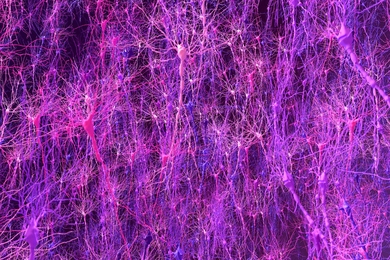
Fragile X study uncovers brain wave biomarker bridging humans and mice
Researchers find mice modeling the autism spectrum disorder fragile X syndrome exhibit the same pattern of differences in low-frequency waves as humans — a new marker for treatment studies.