Zwierlein a winner of DARPA’s Young Faculty Award competition
Will receive two-year research grant of approximately $300,000
New evidence that matter and antimatter may behave differently
Surprising neutrino finding could force physicists to rethink the foundations of particle physics.
Why saliva forms beads on a string
Researchers’ solution to longstanding mystery could enable better inkjet printing and drug-dispensing systems.
15 MIT students awarded DOE-funded Science Graduate Fellowships
Among 150 students nationwide awarded fellowships in program's first year
Shining a light — literally — on diabetes
Device from MIT lab could help diabetic patients monitor their blood glucose levels without finger pricks.
Stringing together a picture of superconductors
MIT physicists use an offshoot of string theory to describe the strange behavior of superconducting materials.
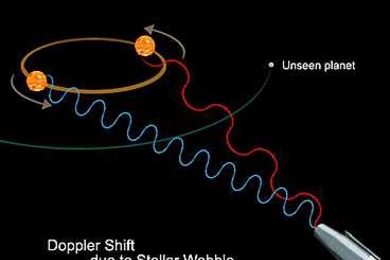
Explained: the Doppler effect
The same phenomenon behind changes in the pitch of a moving ambulance’s siren is helping astronomers locate and study distant planets.
Silicon can be made to melt in reverse
Material that shows melting while cooling might someday lead to applications in solar cells and other devices
Explained: Bandgap
Understanding how electrons get excited is crucial to creating solar cells and light-emitting diodes
Explained: Phonons
When trying to control the way heat moves through solids, it is often useful to think of it as a flow of particles.
Explained: Quark-gluon plasma
By colliding particles, physicists hope to recreate the earliest moments of our universe, on a much smaller scale.
Explained: The Carnot Limit
Long before the nature of heat was understood, the fundamental limit of efficiency of heat-based engines was determined