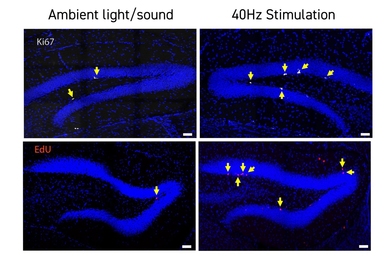
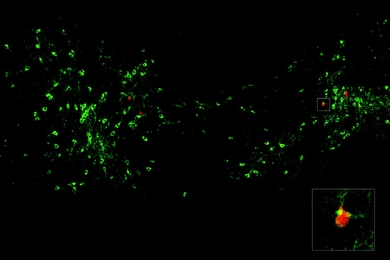
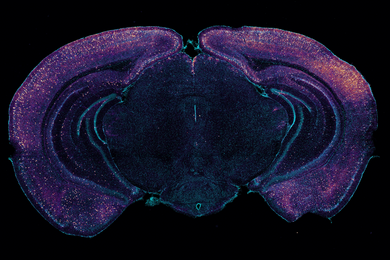
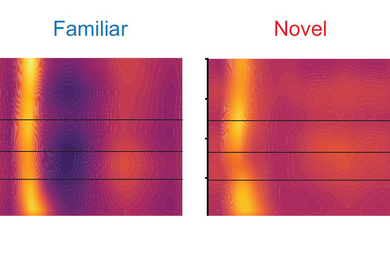
Immune-informed brain aging research offers new treatment possibilities, speakers say
Speakers at MIT’s Aging Brain Initiative symposium described how immune system factors during aging contribute to Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and other conditions. The field is leveraging that knowledge to develop new therapies.