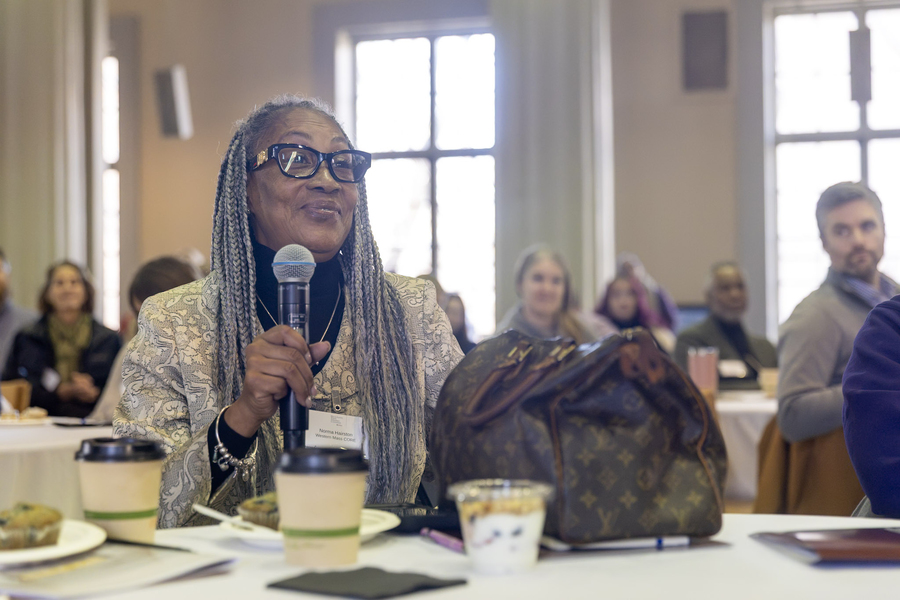
Collaborators from across the Commonwealth of Massachusetts came together in December for a daylong summit of the Massachusetts Prison Education Consortium (MPEC), hosted by the Educational Justice Institute (TEJI) at MIT. Held at MIT’s Walker Memorial, the summit aimed to expand access to high-quality education for incarcerated learners and featured presentations by leaders alongside strategy sessions designed to turn ideas into concrete plans to improve equitable access to higher education and reduce recidivism in local communities.
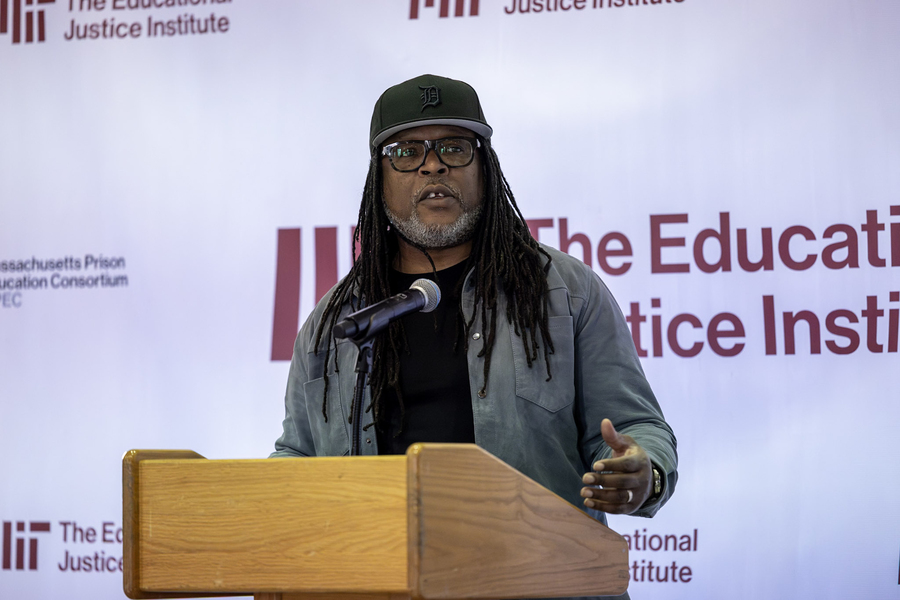
In addition to a keynote address by author and resilience expert Shaka Senghor, speakers such as Molly Lasagna, senior strategy officer in the Ascendium Education Group, and Stefan LoBuglio, former director of the National Institute of Corrections, discussed the roles of learning, healing, and community support in building a more just system for justice-impacted individuals.
The MPEC summit, “Building Integrated Systems Together: Massachusetts Community Colleges and County Corrections 2.0,” addressed three key issues surrounding equitable education: the integration of Massachusetts community college education with county corrections to provide incarcerated individuals with access to higher education; the integration of carceral education with industry to expand work and credentialing opportunities; and the goal of better serving women who experience unique challenges within the criminal legal system.
Created by TEJI, MPEC is a statewide network of Massachusetts colleges, organizations and correctional partners working together to expand access to high-quality, credit-bearing education in Massachusetts prisons and jails. The consortium works on all levels of the pipeline, from academic programming, faculty support, research, reentry pathways, and more, drawing from the research and success of the MIT Prison Education Initiative and the recent restoration of Pell Grant eligibility for incarcerated learners.
The summit was hosted by TEJI co-directors Lee Perlman and Carole Cafferty. Perlman founded the MIT Prison Initiative after years of teaching in MIT’s Experimental Study Group (ESG) and in correctional classrooms. He has been recognized for his work in bringing humanities education to prison settings with three Irwin Sizer Awards and MIT’s Martin Luther King Jr. Leadership Award.
Cafferty jointly co-founded TEJI after more than 30 years’ experience with corrections, including working as superintendent of the Middlesex Jail and House of Correction. She now guides the institute with the knowledge she gained from building integrative and therapeutic educational programs that have since been replicated nationally.
“TEJI serves two populations, incarcerated learners and the MIT community. All of our classes involve MIT students, either learning alongside the incarcerated students or as TAs [teaching assistants],” emphasizes Perlman. In discussing the unification of TEJI with the roles and experiences MIT students take, Perlman further notes: “Our humanities classes, which we call our philosophical life skills curriculum, give MIT students the opportunity to discuss how we want to live our lives with incarcerated students with very different backgrounds.”
These courses, offered through ESG, are subjects with a unique focus that often differ from the traditional focus of a more academic course, often prioritizing hands-on learning and innovative teaching methods. Perlman’s courses are almost always taught in a carceral setting, and he notes that these courses can be highly impactful on the MIT community: “In courses like Philosophy of Love; Non-violence as a Way of Life; and Authenticity and Emotional Intelligence for Teams, the discussions are rich and personal. Many MIT students have described their experience in these classes as life-changing.”
Throughout morning addresses and afternoon strategy sessions, summit attendees developed concrete plans for scaling classroom capacity, aligning curricula with regional labor markets, and strengthening academic and reentry supports that help students remain on the right path after release. Panels explored practical issues, such as how to coordinate registration and credit transfer when a student moves between facilities and how to staff hybrid classrooms that combine in-person and remote instruction, as well as how to measure program outcomes beyond enrollment.
Co-directors Perlman and Cafferty highlighted that the average length of stay within these programs in county facilities is only six months, and that inspired a particular focus on making sure these programs are high-impact even when community members are only able to participate for a short period of time.
Speakers repeatedly emphasized that these logistical challenges often sit atop deeper, more human challenges. In his keynote, Shaka Senghor traced his own journey from trauma to transformation, stressing the power of reading, mentorship, and completing something of one’s own. “What else can you do with your mind?” he asked, describing the moment he realized that the act of reading and writing could change the trajectory of his life.
The line became a refrain throughout the day, a question that caused all to reflect on how prison education could not only function as a workforce pathway, but as a catalyst for dignity and hope after reentry. Senghor also directly confronted the stigma that returning citizens face. “They said I’d be back in prison in six months,” he recalled, using the remark from a corrections officer from the day he was released on parole as a reminder of the structural and social barriers encountered after release.
The summit also brought together funders and implementers who are shaping the field’s future. Molly Lasagna of Ascendium Education Group described the organization’s strategy of “Expand, Support, Connect,” which funds the creation of new educational programs, strengthens basic needs and advising infrastructure, and ensures that individuals leaving prison can transition into high-quality employment opportunities. “How is this education program putting somebody on a pathway to opportunity?” she asked, noting that true change requires aligning education, reentry, and workforce systems.
Participants also heard from Stefan LoBuglio, former director of the National Institute of Corrections and a national thought leader in corrections and reentry, who lauded Massachusetts as a leader while cautioning that staffing shortages, limited program space, and uneven access to technology continue to constrain progress. “We have a crisis in staffing in corrections that does affect our educational programs,” he noted, calling for attention to staff wellness and institutional support as essential components of sustainability.
Throughout the day, TEJI and MPEC leaders highlighted emerging pilots and partnerships, including a new “Prisons to Pathways” initiative aimed at building stackable, transferable credentials aligned with regional industry needs. Additional collaborations with the American Institutes for Research will support new implementation guides and technical assistance resources designed by practitioners in the field.
The summit concluded with a commitment to sustain collaboration. As Senghor reminded participants, the work is both practical and moral. The question he posed, “What else can you do with your mind?,” serves as a reminder to Massachusetts educators, corrections partners, funders, and community organizations to ensure that learning inside prison becomes a foundation for opportunity outside it.