More than 200 years ago, the steam boiler helped spark the Industrial Revolution. Since then, steam has been the lifeblood of industrial activity around the world. Today the production of steam — created by burning gas, oil, or coal to boil water — accounts for a significant percentage of global energy use in manufacturing, powering the creation of paper, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food, and more.
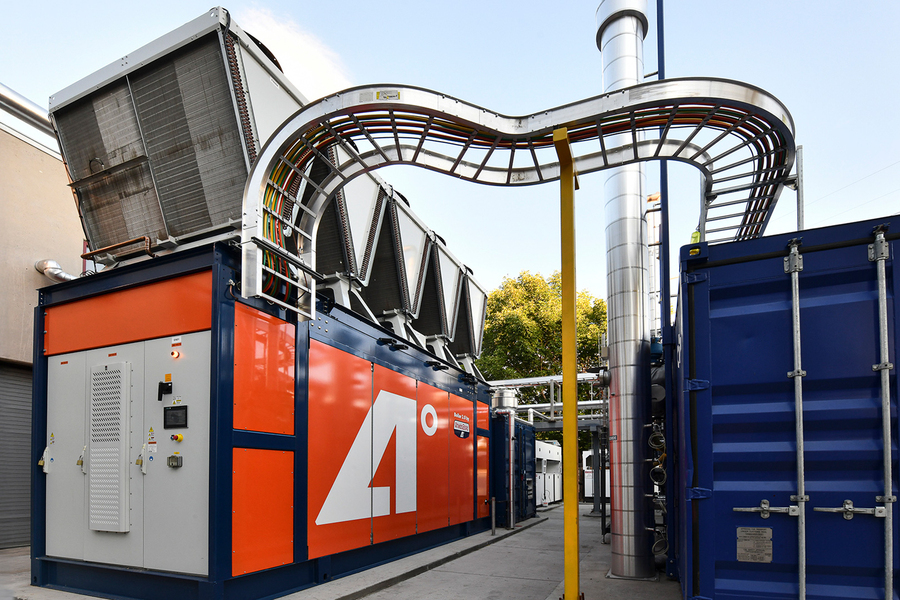
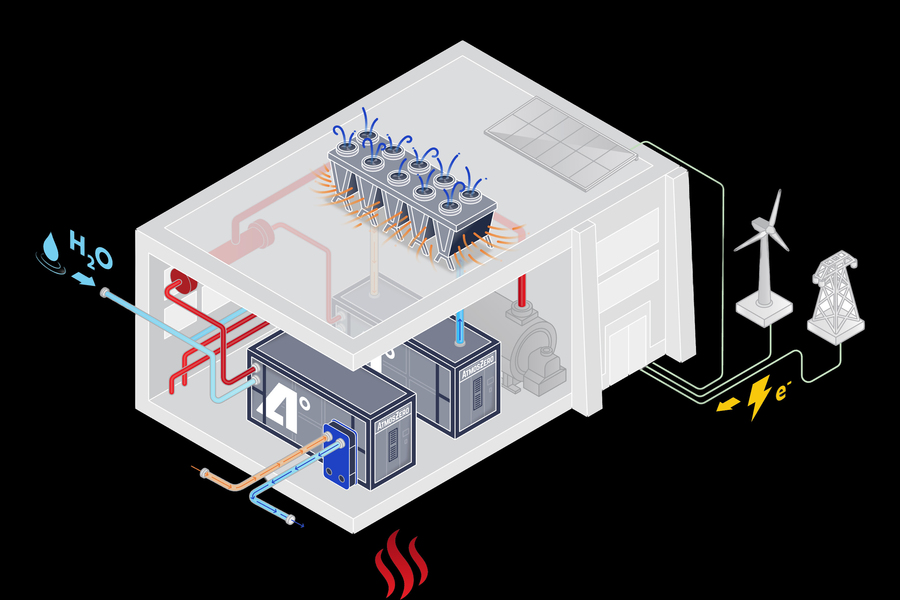
Now, the startup AtmosZero, founded by Addison Stark SM ’10, PhD ’14; Todd Bandhauer; and Ashwin Salvi, is taking a new approach to electrify the centuries-old steam boiler. The company has developed a modular heat pump capable of delivering industrial steam at temperatures up to 150 degrees Celsius to serve as a drop-in replacement for combustion boilers.
The company says its first 1-megawatt steam system is far cheaper to operate than commercially available electric solutions thanks to ultra-efficient compressor technology, which uses 50 percent less electricity than electric resistive boilers. The founders are hoping that’s enough to make decarbonized steam boilers drive the next industrial revolution.
“Steam is the most important working fluid ever,” says Stark, who serves as AtmosZero’s CEO. “Today everything is built around the ubiquitous availability of steam. Cost-effectively electrifying that requires innovation that can scale. In other words, it requires a mass-produced product — not one-off projects.”
Tapping into steam
Stark joined the Technology and Policy Program when he came to MIT in 2007. He ultimately completed a dual master’s degree by adding mechanical engineering to his studies.
“I was interested in the energy transition and in accelerating solutions to enable that,” Stark says. “The transition isn’t happening in a vacuum. You need to align economics, policy, and technology to drive that change.”
Stark stayed at MIT to earn his PhD in mechanical engineering, studying thermochemical biofuels.
After MIT, Stark began working on early-stage energy technologies with the Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency— Energy (ARPA-E), with a focus on manufacturing efficiency, the energy-water nexus, and electrification.
“Part of that work involved applying my training at MIT to things that hadn’t really been innovated on for 50 years,” Stark says. “I was looking at the heat exchanger. It’s so fundamental. I thought, ‘How might we reimagine it in the context of modern advances in manufacturing technology?’”
The problem is as difficult as it is consequential, touching nearly every corner of the global industrial economy. More than 2.2 gigatons of CO2 emissions are generated each year to turn water into steam — accounting for more than 5 percent of global energy-related emissions.
In 2020, Stark co-authored an article in the journal Joule with Gregory Thiel SM ’12, PhD ’15 titled, “To decarbonize industry, we must decarbonize heat.” The article examined opportunities for industrial heat decarbonization, and it got Stark excited about the potential impact of a standardized, scalable electric heat pump.
Most electric boiler options today bring huge increases in operating costs. Many also make use of factory waste heat, which requires pricey retrofits. Stark never imagined he’d become an entrepreneur, but he soon realized no one was going to act on his findings for him.
“The only path to seeing this invention brought out into the world was to found and run the company,” Stark says. “It’s something I didn’t anticipate or necessarily want, but here I am.”
Stark partnered with former ARPA-E awardee Todd Bandhauer, who had been inventing new refrigerant compressor technology in his lab at Colorado State University, and former ARPA-E colleague Ashwin Salvi. The team officially founded AtmosZero in 2022.
“The compressor is the engine of the heat pump and defines the efficiency, cost, and performance,” Stark says. “The fundamental challenge of delivering heat is that the higher your heat pump is raising the air temperature, the lower your maximum efficiency. It runs into thermodynamic limitations. By designing for optimum efficiency in the operational windows that matter for the refrigerants we’re using, and for the precision manufacturing of our compressors, we’re able to maximize the individual stages of compression to maximize operational efficiency.”
The system can work with waste heat from air or water, but it doesn’t need waste heat to work. Many other electric boilers rely on waste heat, but Stark thinks that adds too much complexity to installation and operations.
Instead, in AtmosZero’s novel heat pump cycle, heat from ambient-temperature air is used to warm a liquid heat transfer material, which evaporates a refrigerant so it flows into the system’s series of compressors and heat exchangers, reaching high enough temperatures to boil water while recovering heat from the refrigerant once it reaches lower temperatures. The system can be ramped up and down to seamlessly fit into existing industrial processes.
“We can work just like a combustion boiler,” Stark says. “At the end of the day, customers don’t want to change how their manufacturing facilities operate in order to electrify. You can’t change or increase complexity on-site.”
That approach means the boiler can be deployed in a range of industrial contexts without unique project costs or other changes.
“What we really offer is flexibility and something that can drop in with ease and minimize total capital costs,” Stark says.
From 1 to 1,000
AtmosZero already has a pilot 650 kilowatt system operating at a customer facility near its headquarters in Loveland, Colorado. The company is currently focused on demonstrating year-round durability and reliability of the system as they work to build out their backlog of orders and prepare to scale.
Stark says once the system is brought to a customer’s facility, it can be installed in an afternoon and deployed in a matter of days, with zero downtime.
AtmosZero is aiming to deliver a handful of units to customers over the next year or two, with plans to deploy hundreds of units a year after that. The company is currently targeting manufacturing plants using under 10 megawatts of thermal energy at peak demand, which represents most U.S. manufacturing facilities.
Stark is proud to be part of a growing group of MIT-affiliated decarbonization startups, some of which are targeting specific verticals, like Boston Metal for steel and Sublime Systems for cement. But he says beyond the most common materials, the industry gets very fragmented, with one of the only common threads being the use of steam.
“If we look across industrial segments, we see the ubiquity of steam,” Stark says. “It’s a tremendously ripe opportunity to have impact at scale. Steam cannot be removed from industry. So much of every industrial process that we’ve designed over the last 160 years has been around the availability of steam. So, we need to focus on ways to deliver low-emissions steam rather than removing it from the equation.”