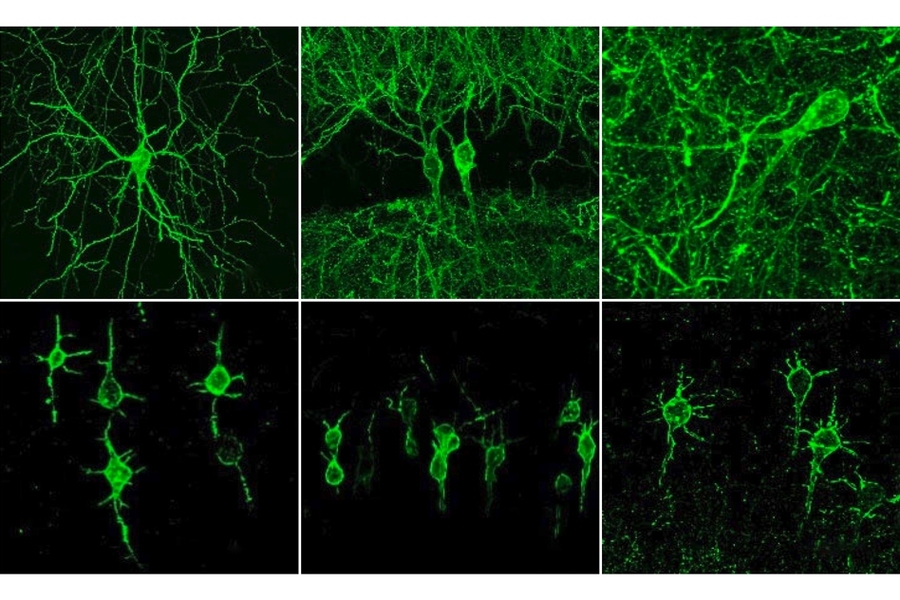
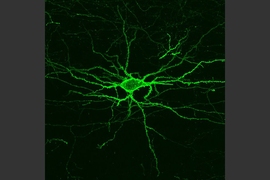
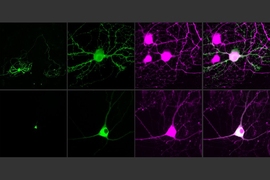
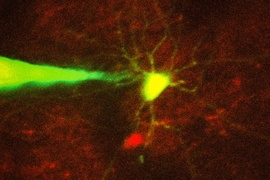
Using a fluorescent probe that lights up when brain cells are electrically active, MIT and Boston University researchers have shown that they can image the activity of many neurons at once, in the brains of mice.
This technique, which can be performed using a simple light microscope, could allow neuroscientists to visualize the activity of circuits within the brain and link them to specific behaviors, says Edward Boyden, the Y. Eva Tan Professor in Neurotechnology and a professor of biological engineering and of brain and cognitive sciences at MIT.
“If you want to study a behavior, or a disease, you need to image the activity of populations of neurons because they work together in a network,” says Boyden, who is also a member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research, Media Lab, and Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research.
Using this voltage-sensing molecule, the researchers showed that they could record electrical activity from many more neurons than has been possible with any existing, fully genetically encoded, fluorescent voltage probe.
Boyden and Xue Han, an associate professor of biomedical engineering at Boston University, are the senior authors of the study, which appears in the Oct. 9 online edition of Nature. The lead authors of the paper are MIT postdoc Kiryl Piatkevich, BU graduate student Seth Bensussen, and BU research scientist Hua-an Tseng.
Seeing connections
Neurons compute using rapid electrical impulses, which underlie our thoughts, behavior, and perception of the world. Traditional methods for measuring this electrical activity require inserting an electrode into the brain, a process that is labor-intensive and usually allows researchers to record from only one neuron at a time. Multielectrode arrays allow the monitoring of electrical activity from many neurons at once, but they don’t sample densely enough to get all the neurons within a given volume. Calcium imaging does allow such dense sampling, but it measures calcium, an indirect and slow measure of neural electrical activity.
In 2018, Boyden’s team developed an alternative way to monitor electrical activity by labeling neurons with a fluorescent probe. Using a technique known as directed protein evolution, his group engineered a molecule called Archon1 that can be genetically inserted into neurons, where it becomes embedded in the cell membrane. When a neuron’s electrical activity increases, the molecule becomes brighter, and this fluorescence can be seen with a standard light microscope.
In the 2018 paper, Boyden and his colleagues showed that they could use the molecule to image electrical activity in the brains of transparent worms and zebrafish embryos, and also in mouse brain slices. In the new study, they wanted to try to use it in living, awake mice as they engaged in a specific behavior.
To do that, the researchers had to modify the probe so that it would go to a subregion of the neuron membrane. They found that when the molecule inserts itself throughout the entire cell membrane, the resulting images are blurry because the axons and dendrites that extend from neurons also fluoresce. To overcome that, the researchers attached a small peptide that guides the probe specifically to membranes of the cell bodies of neurons. They called this modified protein SomArchon.
“With SomArchon, you can see each cell as a distinct sphere,” Boyden says. “Rather than having one cell’s light blurring all its neighbors, each cell can speak by itself loudly and clearly, uncontaminated by its neighbors.”
The researchers used this probe to image activity in a part of the brain called the striatum, which is involved in planning movement, as mice ran on a ball. They were able to monitor activity in several neurons simultaneously and correlate each one’s activity with the mice’s movement. Some neurons’ activity went up when the mice were running, some went down, and others showed no significant change.
“Over the years, my lab has tried many different versions of voltage sensors, and none of them have worked in living mammalian brains until this one,” Han says.
Using this fluorescent probe, the researchers were able to obtain measurements similar to those recorded by an electrical probe, which can pick up activity on a very rapid timescale. This makes the measurements more informative than existing techniques such as imaging calcium, which neuroscientists often use as a proxy for electrical activity.
“We want to record electrical activity on a millisecond timescale,” Han says. “The timescale and activity patterns that we get from calcium imaging are very different. We really don’t know exactly how these calcium changes are related to electrical dynamics.”
With the new voltage sensor, it is also possible to measure very small fluctuations in activity that occur even when a neuron is not firing a spike. This could help neuroscientists study how small fluctuations impact a neuron’s overall behavior, which has previously been very difficult in living brains, Han says.
The study “introduces a new and powerful genetic tool” for imaging voltage in the brains of awake mice, says Adam Cohen, a professor of chemistry, chemical biology, and physics at Harvard University.
“Previously, researchers had to impale neurons with fine glass capillaries to make electrical recordings, and it was only possible to record from one or two cells at a time. The Boyden team recorded from about 10 cells at a time. That’s a lot of cells,” says Cohen, who was not involved in the research. “These tools open new possibilities to study the statistical structure of neural activity. But a mouse brain contains about 75 million neurons, so we still have a long way to go.”
Mapping circuits
The researchers also showed that this imaging technique can be combined with optogenetics — a technique developed by the Boyden lab and collaborators that allows researchers to turn neurons on and off with light by engineering them to express light-sensitive proteins. In this case, the researchers activated certain neurons with light and then measured the resulting electrical activity in these neurons.
This imaging technology could also be combined with expansion microscopy, a technique that Boyden’s lab developed to expand brain tissue before imaging it, make it easier to see the anatomical connections between neurons in high resolution.
“One of my dream experiments is to image all the activity in a brain, and then use expansion microscopy to find the wiring between those neurons,” Boyden says. “Then can we predict how neural computations emerge from the wiring.”
Such wiring diagrams could allow researchers to pinpoint circuit abnormalities that underlie brain disorders, and may also help researchers to design artificial intelligence that more closely mimics the human brain, Boyden says.
The MIT portion of the research was funded by Edward and Kay Poitras, the National Institutes of Health, including a Director’s Pioneer Award, Charles Hieken, John Doerr, the National Science Foundation, the HHMI-Simons Faculty Scholars Program, the Human Frontier Science Program, and the U.S. Army Research Office.