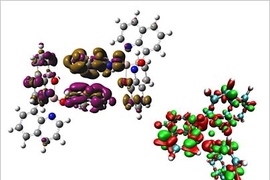
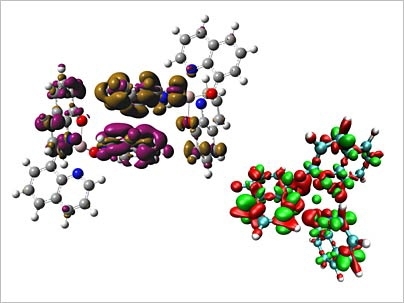
Troy Van Voorhis likes to watch how things work. This natural curiosity led to his current research on the behavior of electrons and how they function in various molecular systems, including artificial photosynthesis. The theories and simulations he and his team create may help lead to improvements in devices such as electronics, solar cells and lighting.
Now the MIT assistant professor of chemistry will have more opportunities to explore new simulations. Van Voorhis is one of 20 promising researchers recently awarded the 2006 David and Lucile Packard Foundation fellowship. He will receive an unrestricted research grant of $625,000 over five years.
"This frees me long-term to develop methods to make reliable predictions about the transfer of electrons, which is the most basic chemical reaction," said Van Voorhis, 30. "It is difficult to simulate the changes in electronic structure that accompany electron transfer, because a reaction pushes the electrons out of equilibrium, and current techniques for describing this are not adequate."
Van Voorhis and his team are developing methods and computer software that can simulate what happens when a dot in a light-emitting diode (LED) of a computer display turns on. In the case of an optical LED, positive and negative charges are strongly attracted to one another and become trapped. The unusual rules of quantum physics dictate that the charges can only recombine to emit light if they are spinning in opposite directions. As a result, typically only 25 percent of the trapped charges produce light; the other 75 percent of the charges spin in the same direction and are essentially wasted.
Van Voorhis and his colleagues have developed a computer program that simulates how these coupled spinning charges are nudged to react and thus emit light. The simulations indicate that the emission will increase if some of the charges spinning in one direction can be turned into charges spinning in the opposite direction and then form stable pairs.
"This situation could be selectively created in optical LEDs to improve the efficiency of a device such as a display," he said.
There are also potential applications of these visualization techniques to electronic devices, pharmaceuticals, energy and other fields, but they still are far off in the future.
Another big challenge being tackled by the Van Voorhis group is understanding and simulating the process of photosynthesis. In plant photosynthesis, light reacts with carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar and oxygen, which humans can later burn to produce energy. The knowledge of how to artificially mimic a process like photosynthesis could help scientists figure out a way to efficiently store solar energy in molecules that last for long periods.
The challenge is that the bonds being broken in any photosynthetic process are very strong. By breaking these strong bonds and forming weaker ones, molecules with higher energy are created. These molecules store the energy harvested from sunlight, and this energy is later released when the high-energy molecules are burned. However, current methods for artificial photosynthesis waste too much energy in breaking the strong bonds. Van Voorhis hopes to understand how to break bonds more efficiently so that a larger portion of the valuable energy is stored in the product molecules.
"We only have a partial knowledge of what is going on in photosynthesis," Van Voorhis said. "If you don't know exactly how something works, you don't know how to improve it."
To improve this state of affairs, his lab has been studying how electrons create and destroy chemical bonds. The new funding from the Packard Fellowship will allow him to move to the next step and start researching how to get light to turn into energy that won't escape as heat.
A version of this article appeared in MIT Tech Talk on November 22, 2006 (download PDF).