New software designs eco-friendly clothing that can reassemble into new items
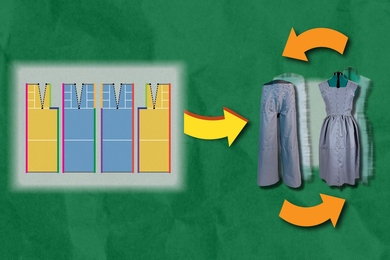
To reduce waste, the Refashion program helps users create outlines for adaptable clothing, such as pants that can be reconfigured into a dress. Each component of these pieces can be replaced, rearranged, or restyled.