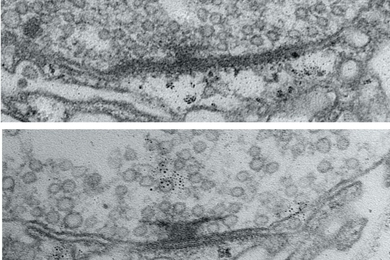
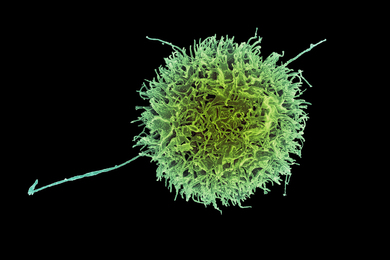
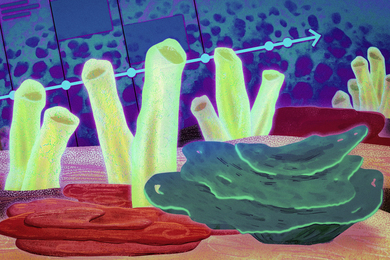
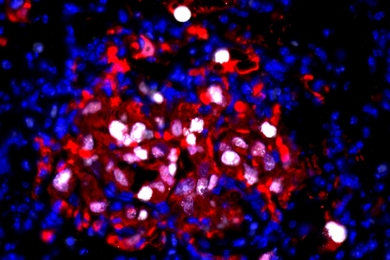
Neural activity helps circuit connections mature into optimal signal transmitters
Scientists identified how circuit connections in fruit flies tune to the right size and degree of signal transmission capability. Understanding this could lead to a way to tweak abnormal signal transmission in certain disorders.