Using tiny gold particles and infrared light, MIT researchers have developed a drug-delivery system that allows multiple drugs to be released in a controlled fashion.
Such a system could one day be used to provide more control when battling diseases commonly treated with more than one drug, according to the researchers.
"With a lot of diseases, especially cancer and AIDS, you get a synergistic effect with more than one drug," said Kimberly Hamad-Schifferli, assistant professor of biological and mechanical engineering and senior author of a paper on the work that recently appeared in the journal ACS Nano.
Delivery devices already exist that can release two drugs, but the timing of the release must be built into the device -- it cannot be controlled from outside the body. The new system is controlled externally and theoretically could deliver up to three or four drugs.
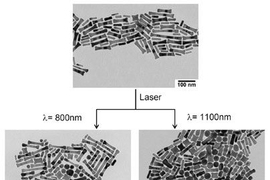
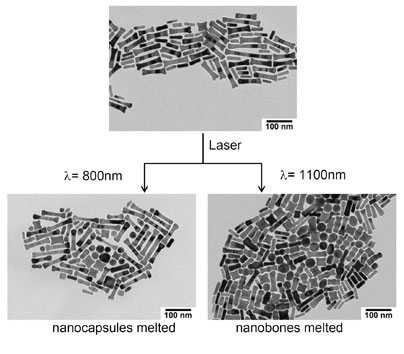
The new technique takes advantage of the fact that when gold nanoparticles are exposed to infrared light, they melt and release drug payloads attached to their surfaces.
Nanoparticles of different shapes respond to different infrared wavelengths, so "just by controlling the infrared wavelength, we can choose the release time" for each drug, said Andy Wijaya, graduate student in chemical engineering and lead author of the paper.
The team built two different shapes of nanoparticles, which they call "nanobones" and "nanocapsules." Nanobones melt at light wavelengths of 1,100 nanometers, and nanocapsules at 800 nanometers.
In the ACS Nano study, the researchers tested the particles with a payload of DNA. Each nanoparticle can carry hundreds of strands of DNA, and could also be engineered to transport other types of drugs.
In theory, up to four different-shaped particles could be developed, each releasing its payload at different wavelengths.
Other authors of the paper are Stefan Schaffer and Ivan Pallares, who were National Science Foundation REU (Research Experiences for Undergraduates) summer students through the MIT Department of Biological Engineering in 2008.
A version of this article appeared in MIT Tech Talk on January 14, 2009 (download PDF).