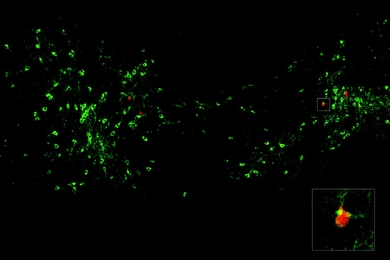
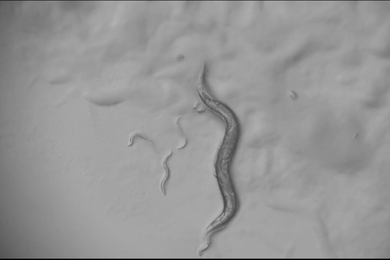
How an MIT professor introduced hundreds of thousands of students to neuroscience
With an emphasis on approachability, Professor Mark Bear’s “Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain” enters its fourth decade as the text of undergraduate neuroscience classes worldwide.