Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
A plane that lands like a bird
An innovative control system allows a foam glider to touch down on a perch or a wire like a pet parakeet.
Broadband picture may not be so bleak
A new study disputes the claim that Internet data rates in the U.S. are only half as high as advertised; study’s authors call for better data.
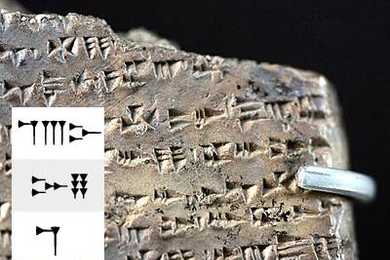
Computer automatically deciphers ancient language
A new system that took a couple hours to decipher much of the ancient language Ugaritic could help improve online translation software.
Toward the Semantic Web
A new standard from the World Wide Web Consortium brings the Web a step closer to realizing the vision of its inventor, Tim Berners-Lee.
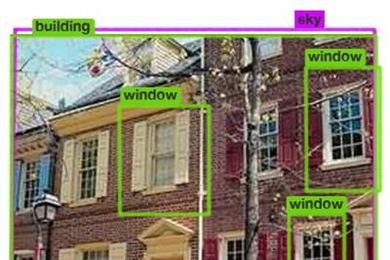
How the brain recognizes objects
A new computational model sheds light on the workings of the human visual system and could help advance artificial-intelligence research, too.
Gesture-based computing on the cheap
With a single piece of inexpensive hardware — a multicolored glove — MIT researchers are making Minority Report-style interfaces more accessible.
Rivest wins faculty’s Killian Award
MIT encryption pioneer recognized for ‘extraordinary’ contributions in computer science
Machines that learn better
New math will make it much easier to build machine-learning systems that tackle a wider range of problems.
When good enough is better
By exploiting a simple but counterintuitive trick, a new system finds sections of computer programs where accuracy can be traded for speed.
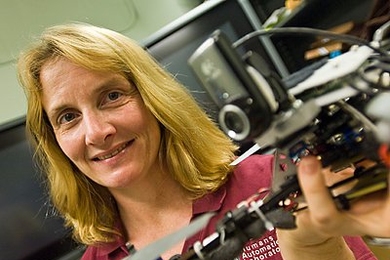
In Profile: Missy Cummings
Former U.S. Naval fighter pilot aims to improve how humans and computers interact.
Web sites that can take a punch
By preventing web applications from deviating from their normal behavior, a new MIT system can keep them online even during a cyberattack.
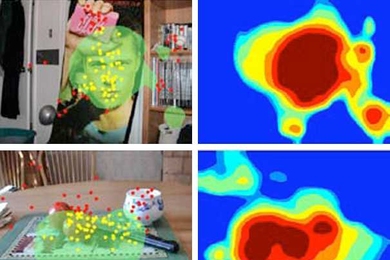
Context is ev … well, something, anyway
MIT research uses information about how frequently objects are seen together to refine the conclusions of object recognition systems.
Explained: Linear and nonlinear systems
Much scientific research across a range of disciplines tries to find linear approximations of nonlinear behaviors. But what does that mean?