Audio
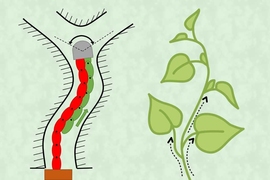
In the horticultural world, some vines are especially grabby. As they grow, the woody tendrils can wrap around obstacles with enough force to pull down entire fences and trees.
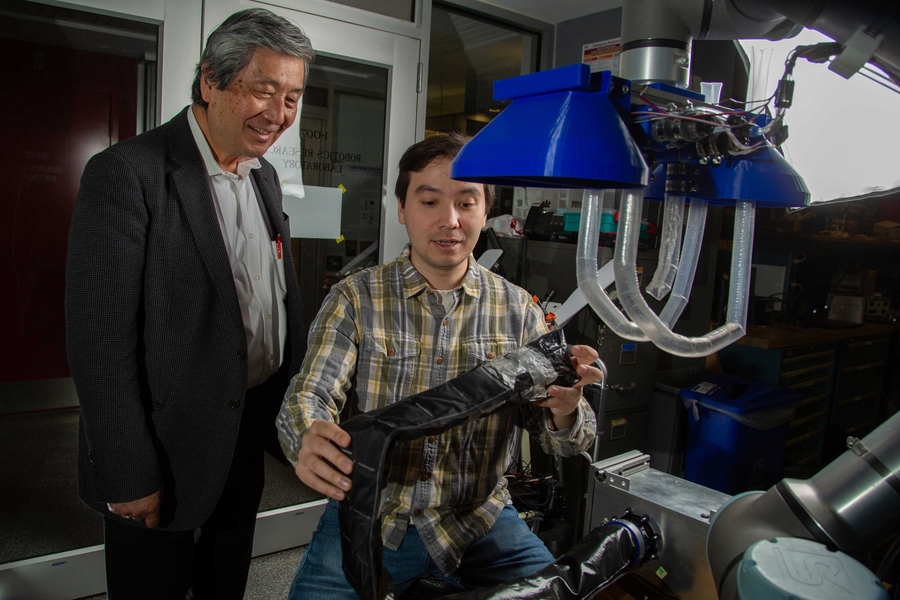
Inspired by vines’ twisty tenacity, engineers at MIT and Stanford University have developed a robotic gripper that can snake around and lift a variety of objects, including a glass vase and a watermelon, offering a gentler approach compared to conventional gripper designs. A larger version of the robo-tendrils can also safely lift a human out of bed.
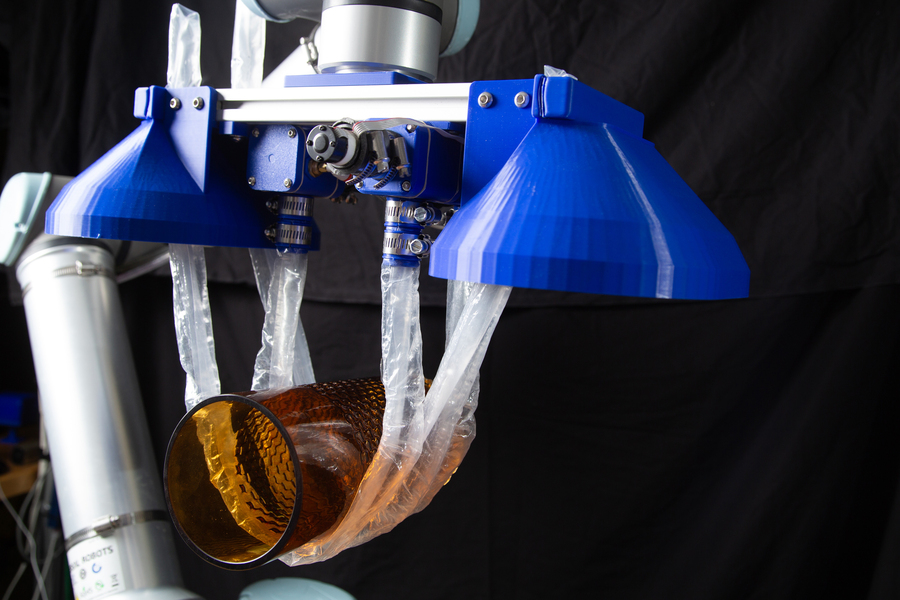
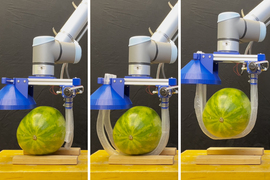
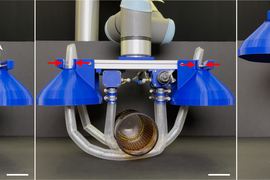
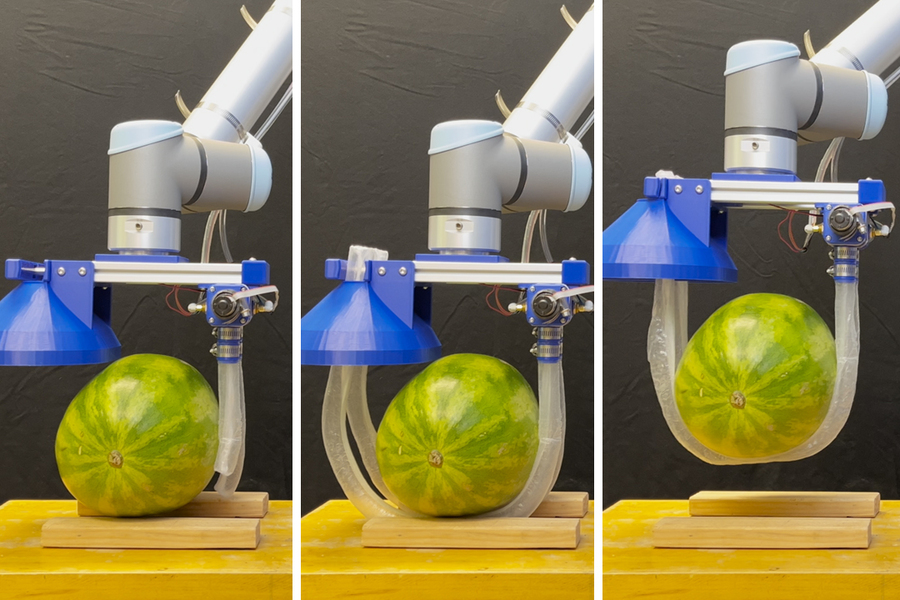
The new bot consists of a pressurized box, positioned near the target object, from which long, vine-like tubes inflate and grow, like socks being turned inside out. As they extend, the vines twist and coil around the object before continuing back toward the box, where they are automatically clamped in place and mechanically wound back up to gently lift the object in a soft, sling-like grasp.
The researchers demonstrated that the vine robot can safely and stably lift a variety of heavy and fragile objects. The robot can also squeeze through tight quarters and push through clutter to reach and grasp a desired object.
The team envisions that this type of robot gripper could be used in a wide range of scenarios, from agricultural harvesting to loading and unloading heavy cargo. In the near term, the group is exploring applications in eldercare settings, where soft inflatable robotic vines could help to gently lift a person out of bed.
“Transferring a person out of bed is one of the most physically strenuous tasks that a caregiver carries out,” says Kentaro Barhydt, a PhD candidate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering. “This kind of robot can help relieve the caretaker, and can be gentler and more comfortable for the patient.”
Barhydt, along with his co-first author from Stanford, O. Godson Osele, and their colleagues, present the new robotic design today in the journal Science Advances. The study’s co-authors are Harry Asada, the Ford Professor of Engineering at MIT, and Allison Okamura, the Richard W. Weiland Professor of Engineering at Stanford University, along with Sreela Kodali and Cosmia du Pasquier at Stanford University, and former MIT graduate student Chase Hartquist, now at the University of Florida, Gainesville.
Open and closed

Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
The team’s Stanford collaborators, led by Okamura, pioneered the development of soft, vine-inspired robots that grow outward from their tips. These designs are largely built from thin yet sturdy pneumatic tubes that grow and inflate with controlled air pressure. As they grow, the tubes can twist, bend, and snake their way through the environment, and squeeze through tight and cluttered spaces.
Researchers have mostly explored vine robots for use in safety inspections and search and rescue operations. But at MIT, Barhydt and Asada, whose group has developed robotic aides for the elderly, wondered whether such vine-inspired robots could address certain challenges in eldercare — specifically, the challenge of safely lifting a person out of bed. Often in nursing and rehabilitation settings, this transfer process is done with a patient lift, operated by a caretaker who must first physically move a patient onto their side, then back onto a hammock-like sheet. The caretaker straps the sheet around the patient and hooks it onto the mechanical lift, which then can gently hoist the patient out of bed, similar to suspending a hammock or sling.
The MIT and Stanford team imagined that as an alternative, a vine-like robot could gently snake under and around a patient to create its own sort of sling, without a caretaker having to physically maneuver the patient. But in order to lift the sling, the researchers realized they would have to add an element that was missing in existing vine robot designs: Essentially, they would have to close the loop.
Most vine-inspired robots are designed as “open-loop” systems, meaning they act as open-ended strings that can extend and bend in different configurations, but they are not designed to secure themselves to anything to form a closed loop. If a vine robot could be made to transform from an open loop to a closed loop, Barhydt surmised that it could make itself into a sling around the object and pull itself up, along with whatever, or whomever, it might hold.
For their new study, Barhydt, Osele, and their colleagues outline the design for a new vine-inspired robotic gripper that combines both open- and closed-loop actions. In an open-loop configuration, a robotic vine can grow and twist around an object to create a firm grasp. It can even burrow under a human lying on a bed. Once a grasp is made, the vine can continue to grow back toward and attach to its source, creating a closed loop that can then be retracted to retrieve the object.
“People might assume that in order to grab something, you just reach out and grab it,” Barhydt says. “But there are different stages, such as positioning and holding. By transforming between open and closed loops, we can achieve new levels of performance by leveraging the advantages of both forms for their respective stages.”
Gentle suspension
As a demonstration of their new open- and closed-loop concept, the team built a large-scale robotic system designed to safely lift a person up from a bed. The system comprises a set of pressurized boxes attached on either end of an overhead bar. An air pump inside the boxes slowly inflates and unfurls thin vine-like tubes that extend down toward the head and foot of a bed. The air pressure can be controlled to gently work the tubes under and around a person, before stretching back up to their respective boxes. The vines then thread through a clamping mechanism that secures the vines to each box. A winch winds the vines back up toward the boxes, gently lifting the person up in the process.
“Heavy but fragile objects, such as a human body, are difficult to grasp with the robotic hands that are available today,” Asada says. “We have developed a vine-like, growing robot gripper that can wrap around an object and suspend it gently and securely.”
"There’s an entire design space we hope this work inspires our colleagues to continue to explore,” says co-lead author Osele. “I especially look forward to the implications for patient transfer applications in health care.”
“I am very excited about future work to use robots like these for physically assisting people with mobility challenges,” adds co-author Okamura. “Soft robots can be relatively safe, low-cost, and optimally designed for specific human needs, in contrast to other approaches like humanoid robots.”
While the team’s design was motivated by challenges in eldercare, the researchers realized the new design could also be adapted to perform other grasping tasks. In addition to their large-scale system, they have built a smaller version that can attach to a commercial robotic arm. With this version, the team has shown that the vine robot can grasp and lift a variety of heavy and fragile objects, including a watermelon, a glass vase, a kettle bell, a stack of metal rods, and a playground ball. The vines can also snake through a cluttered bin to pull out a desired object.
“We think this kind of robot design can be adapted to many applications,” Barhydt says. “We are also thinking about applying this to heavy industry, and things like automating the operation of cranes at ports and warehouses.”
This work was supported, in part, by the National Science Foundation and the Ford Foundation.