Peripheral nerves — the network connecting the brain, spinal cord, and central nervous system to the rest of the body — transmit sensory information, control muscle movements, and regulate automatic bodily functions. Bioelectronic devices implanted on these nerves offer remarkable potential for the treatment and rehabilitation of neurological and systemic diseases. However, because the body perceives these implants as foreign objects, they often trigger the formation of dense fibrotic tissue at bioelectronic device–tissue interfaces, which can significantly compromise device performance and longevity.
New research published in the journal Science Advances presents a robust bioadhesive strategy that establishes non-fibrotic bioelectronic interfaces on diverse peripheral nerves — including the occipital, vagus, deep peroneal, sciatic, tibial, and common peroneal nerves — for up to 12 weeks.
“We discovered that adhering the bioelectrodes to peripheral nerves can fully prevent the formation of fibrosis on the interfaces,” says Xuanhe Zhao, the Uncas and Helen Whitaker Professor, and professor of mechanical engineering and civil engineering at MIT. “We further demonstrated long-term, drug-free hypertension mitigation using non-fibrotic bioelectronics over four weeks, and ongoing.”
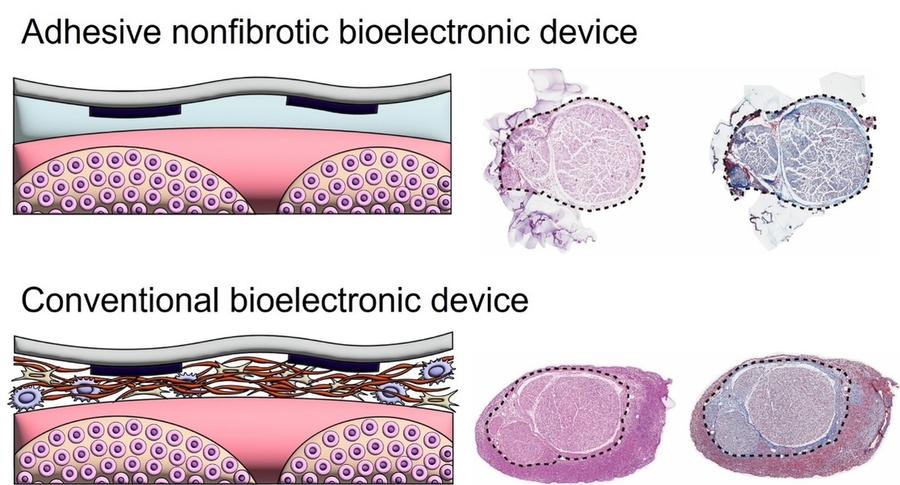
The approach inhibits immune cell infiltration at the device-tissue interface, thereby preventing the formation of fibrous capsules within the inflammatory microenvironment. In preclinical rodent models, the team demonstrated that the non-fibrotic, adhesive bioelectronic device maintained stable, long-term regulation of blood pressure.
“Our long-term blood pressure regulation approach was inspired by traditional acupuncture,” says Hyunmin Moon, lead author of the study and a postdoc in the Department of Mechanical Engineering. “The lower leg has long been used in hypertension treatment, and the deep peroneal nerve lies precisely at an acupuncture point. We were thrilled to see that stimulating this nerve achieved blood pressure regulation for the first time. The convergence of our non-fibrotic, adhesive bioelectronic device with this long-term regulation capability holds exciting promise for translational medicine.”
Importantly, after 12 weeks of implantation with continuous nerve stimulation, only minimal macrophage activity and limited deposition of smooth muscle actin and collagen were detected, underscoring the device’s potential to deliver long-term neuromodulation without triggering fibrosis. “The contrast between the immune response of the adhered device and that of the non-adhered control is striking,” says Bastien Aymon, a study co-author and a PhD candidate in mechanical engineering. “The fact that we can observe immunologically pristine interfaces after three months of adhesive implantation is extremely encouraging for future clinical translation.”
This work offers a broadly applicable strategy for all implantable bioelectronic systems by preventing fibrosis at the device interface, paving the way for more effective and long-lasting therapies such as hypertension mitigation.
Hypertension is a major contributor to cardiovascular diseases, the leading cause of death worldwide. Although medications are effective in many cases, more than 50 percent of patients remain hypertensive despite treatment — a condition known as resistant hypertension. Traditional carotid sinus or vagus nerve stimulation methods are often accompanied by side effects including apnea, bradycardia, cough, and paresthesia.
“In contrast, our non-fibrotic, adhesive bioelectronic device targeting the deep peroneal nerve enables long-term blood pressure regulation in resistant hypertensive patients without metabolic side effects,” says Moon.