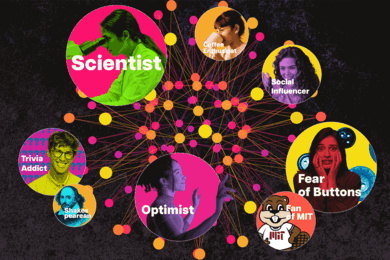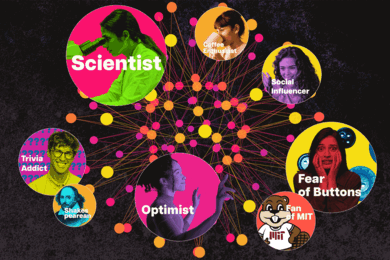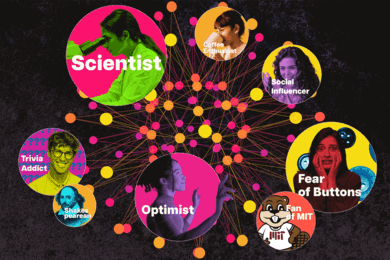
Study: AI chatbots provide less-accurate information to vulnerable users
Research from the MIT Center for Constructive Communication finds leading AI models perform worse for users with lower English proficiency, less formal education, and non-US origins.