A team of researchers has created a new way of manufacturing microstructured surfaces that have novel three-dimensional textures. These surfaces, made by self-assembly of carbon nanotubes, could exhibit a variety of useful properties — including controllable mechanical stiffness and strength, or the ability to repel water in a certain direction.
“We have demonstrated that mechanical forces can be used to direct nanostructures to form complex three-dimensional microstructures, and that we can independently control … the mechanical properties of the microstructures,” says A. John Hart, the Mitsui Career Development Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at MIT and senior author of a paper describing the new technique in the journal Nature Communications.
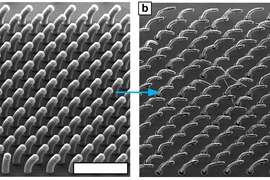
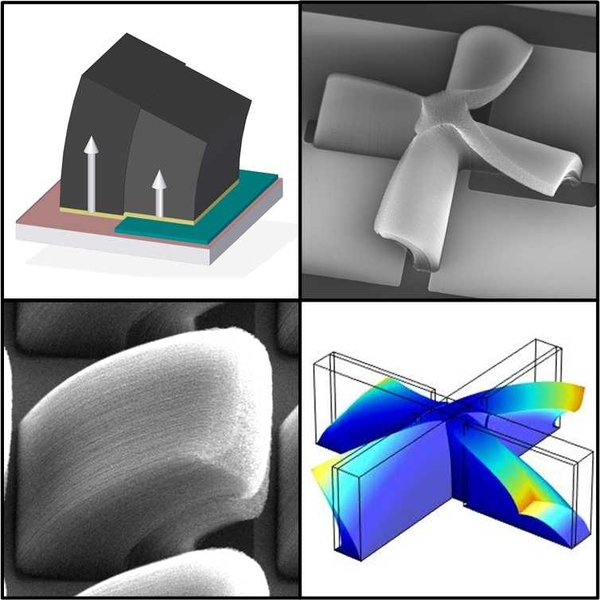
The technique works by inducing carbon nanotubes to bend as they grow. The mechanism is analogous to the bending of a bimetallic strip, used as the control in old thermostats, as it warms: One material expands faster than another bonded to it. But in this new process, the material bends as it is produced by a chemical reaction.
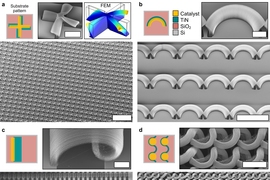
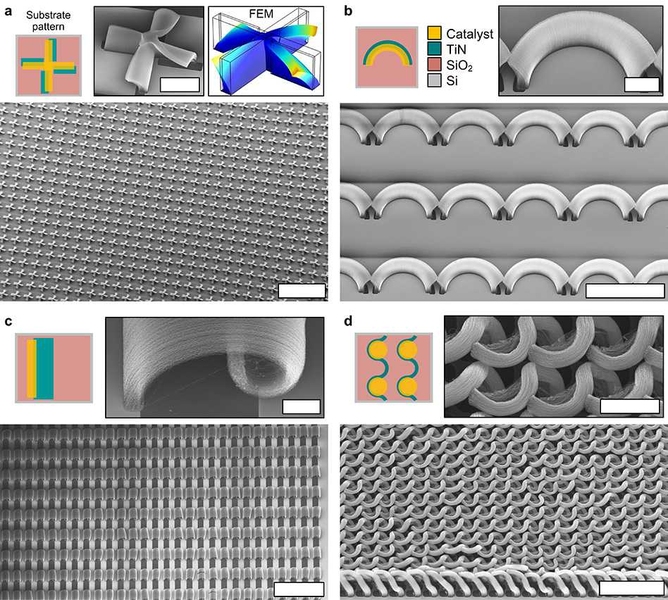
The process begins by printing two patterns onto a substrate: One is a catalyst of carbon nanotubes; the second material modifies the growth rate of the nanotubes. By offsetting the two patterns, the researchers showed that the nanotubes bend into predictable shapes as they extend.
“We can specify these simple two-dimensional instructions, and cause the nanotubes to form complex shapes in three dimensions,” says Hart. Where nanotubes growing at different rates are adjacent, “they push and pull on each other,” producing more complex forms, Hart explains. “It’s a new principle of using mechanics to control the growth of a nanostructured material,” he says.
Few high-throughput manufacturing processes can achieve such flexibility in creating three-dimensional structures, Hart says. This technique, he adds, is attractive because it can be used to create large expanses of the structures simultaneously; the shape of each structure can be specified by designing the starting pattern. Hart says the technique could also enable control of other properties, such as electrical and thermal conductivity and chemical reactivity, by attaching various coatings to the carbon nanotubes after they grow.
“If you coat the structures after the growth process, you can exquisitely modify their properties,” says Hart. For example, coating the nanotubes with ceramic, using a method called atomic layer deposition, allows the mechanical properties of the structures to be controlled. “When a thick coating is deposited, we have a surface with exceptional stiffness, strength, and toughness relative to [its] density,” Hart explains. “When a thin coating is deposited, the structures are very flexible and resilient.”
This approach may also enable “high-fidelity replication of the intricate structures found on the skins of certain plants and animals,” Hart says, and could make it possible to mass-produce surfaces with specialized characteristics, such as the water-repellent and adhesive ability of some insects. “We’re interested in controlling these fundamental properties using scalable manufacturing techniques,” Hart says.
Hart says the surfaces have the durability of carbon nanotubes, which could allow them to survive in harsh environments, and could be connected to electronics and function as sensors of mechanical or chemical signals.
Kevin Turner, an associate professor of mechanical engineering and applied mechanics at the University of Pennsylvania who was not involved in this research, says this approach “is quite novel because it allows for the engineering of complex 3-D microstructures [composed] of carbon nanotubes. Traditional microfabrication approaches, such as patterning and etching, generally only allow for the fabrication of simple 3-D structures that are essentially extruded 2-D patterns.”
Turner adds, “A particularly exciting aspect of this work is that the structures are composed of carbon nanotubes, which have desirable mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties.”
Along with Hart, the research team included Michael de Volder of Cambridge University; Sei Jin Park, a visiting doctoral student from the University of Michigan; and Sameh Tawfick, a former postdoc at MIT who is now at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The work was supported by the European Research Council, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.