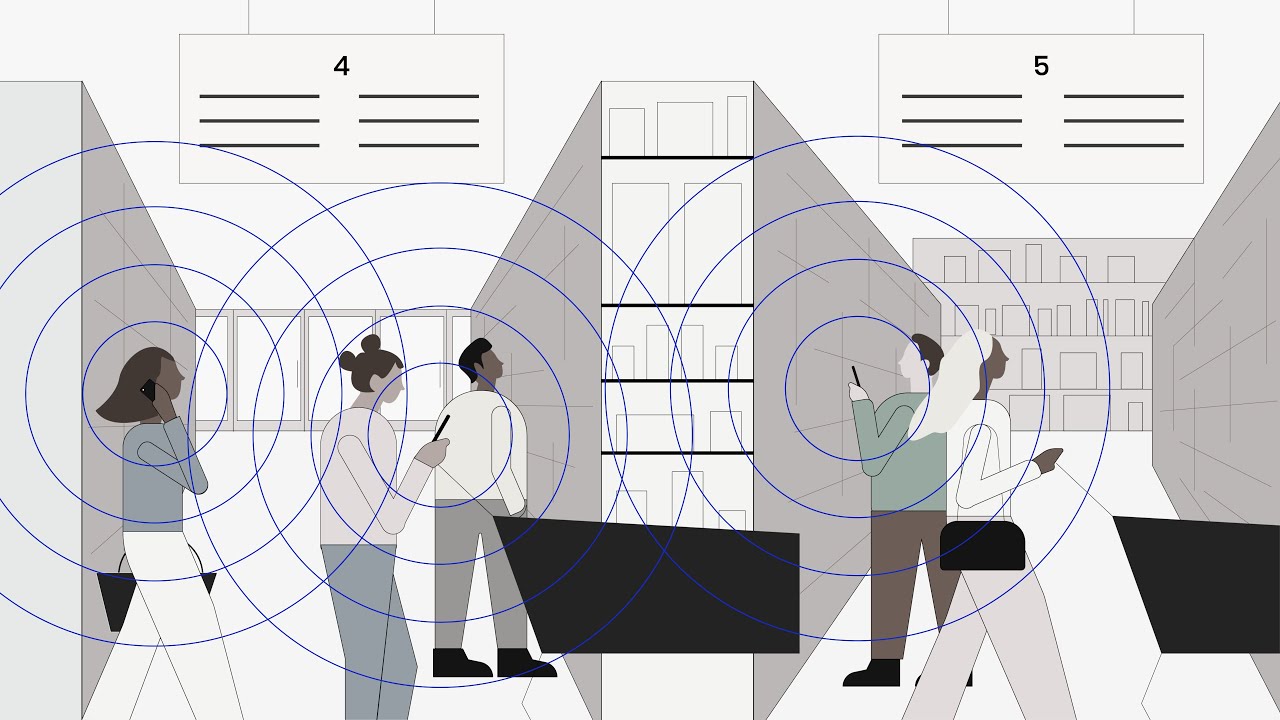
Imagine you’ve been diagnosed as Covid-19 positive. Health officials begin contact tracing to contain infections, asking you to identify people with whom you’ve been in close contact. The obvious people come to mind — your family, your coworkers. But what about the woman ahead of you in line last week at the pharmacy, or the man bagging your groceries? Or any of the other strangers you may have come close to in the past 14 days?
A team led by MIT researchers and including experts from many institutions is developing a system that augments “manual” contact tracing by public health officials, while preserving the privacy of all individuals. The system relies on short-range Bluetooth signals emitted from people’s smartphones. These signals represent random strings of numbers, likened to “chirps” that other nearby smartphones can remember hearing.
If a person tests positive, they can upload the list of chirps their phone has put out in the past 14 days to a database. Other people can then scan the database to see if any of those chirps match the ones picked up by their phones. If there’s a match, a notification will inform that person that they may have been exposed to the virus, and will include information from public health authorities on next steps to take. Vitally, this entire process is done while maintaining the privacy of those who are Covid-19 positive and those wishing to check if they have been in contact with an infected person.
“I keep track of what I’ve broadcasted, and you keep track of what you’ve heard, and this will allow us to tell if someone was in close proximity to an infected person,” says Ron Rivest, MIT Institute Professor and principal investigator of the project. “But for these broadcasts, we’re using cryptographic techniques to generate random, rotating numbers that are not just anonymous, but pseudonymous, constantly changing their ‘ID,’ and that can’t be traced back to an individual.”
This approach to private, automated contact tracing will be available in a number of ways, including through the privacy-first effort launched at MIT in response to Covid-19 called SafePaths. This broad set of mobile apps is under development by a team led by Ramesh Raskar of the MIT Media Lab. The design of the new Bluetooth-based system has benefited from SafePaths’ early work in this area.
Bluetooth exchanges
Smartphones already have the ability to advertise their presence to other devices via Bluetooth. Apple’s “Find My” feature, for example, uses chirps from a lost iPhone or MacBook to catch the attention of other Apple devices, helping the owner of the lost device to eventually find it.
“Find My inspired this system. If my phone is lost, it can start broadcasting a Bluetooth signal that’s just a random number; it’s like being in the middle of the ocean and waving a light. If someone walks by with Bluetooth enabled, their phone doesn’t know anything about me; it will just tell Apple, ‘Hey, I saw this light,’” says Marc Zissman, the associate head of MIT Lincoln Laboratory’s Cyber Security and Information Science Division and co-principal investigator of the project.
With their system, the team is essentially asking a phone to send out this kind of random signal all the time and to keep a log of these signals. At the same time, the phone detects chirps it has picked up from other phones, and only logs chirps that would be medically significant for contact tracing — those emitted from within an approximate 6-foot radius and picked up for a certain duration of time, say 10 minutes.
Phone owners would get involved by downloading an app that enables this system. After a positive diagnosis, a person would receive a QR code from a health official. By scanning the code through that app, that person can upload their log to the cloud. Anyone with the app could then initiate their phones to scan these logs. A notification, if there’s a match, could tell a user how long they were near an infected person and the approximate distance.
Privacy-preserving technology
Some countries most successful at containing the spread of Covid-19 have been using smartphone-based approaches to conduct contact tracing, yet the researchers note these approaches have not always protected individual’s privacy. South Korea, for example, has implemented apps that notify officials if a diagnosed person has left their home, and can tap into people’s GPS data to pinpoint exactly where they’ve been.
“We’re not tracking location, not using GPS, not attaching your personal ID or phone number to any of these random numbers your phone is emitting,” says Daniel Weitzner, a principal research scientist in the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and co-principal investigator of this effort. “What we want is to enable everyone to participate in a shared process of seeing if you might have been in contact, without revealing, or forcing anyone to reveal, anything.”
Choice is key. Weitzner sees the system as a virtual knock on the door that preserves people’s right to not answer it. The hope, though, is that everyone who can opt in would do so to help contain the spread of Covid-19. “We need a large percentage of the population to opt in for this system to really work. We care about every single Bluetooth device out there; it’s really critical to make this a whole ecosystem,” he says.
Public health impact
Throughout the development process, the researchers have worked closely with a medical advisory team to ensure that this system would contribute effectively to contact tracing efforts. This team is led by Louise Ivers, who is an infectious disease expert, associate professor at Harvard Medical School, and executive director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Global Health.
“In order for the U.S. to really contain this epidemic, we need to have a much more proactive approach that allows us to trace more widely contacts for confirmed cases. This automated and privacy-protecting approach could really transform our ability to get the epidemic under control here and could be adapted to have use in other global settings,” Ivers says. “What’s also great is that the technology can be flexible to how public health officials want to manage contacts with exposed cases in their specific region, which may change over time.”
For example, the system could notify someone that they should self-isolate, or it could request that they check in through the app to connect with specialists regarding daily symptoms and well-being. In other circumstances, public health officials could request that this person get tested if they were noticing a cluster of cases.
The ability to conduct contact tracing quickly and at a large scale can be effective not only in flattening the curve of the outbreak, but also for enabling people to safely enter public life once a community is on the downward side of the curve. “We want to be able to let people carefully get back to normal life while also having this ability to carefully quarantine and identify certain vectors of an outbreak,” Rivest says.
Toward implementation
Lincoln Laboratory engineers have led the prototyping of the system. One of the hardest technical challenges has been achieving interoperability, that is, making it possible for a chirp from an iPhone to be picked up by an Android device and vice versa. A test at the laboratory late last week proved that they achieved this capability, and that chirps could be picked up by other phones of various makes and models.
A vital next step toward implementation is engaging with the smartphone manufacturers and software developers — Apple, Google, and Microsoft. “They have a critical role here. The aim of the prototype is to prove to these developers that this is feasible for them to implement,” Rivest says. As those collaborations are forming, the team is also demonstrating its prototype system to state and federal government agencies.
Rivest emphasizes that collaboration has made this project possible. These collaborators include the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Global Health, CSAIL, MIT Lincoln Laboratory, Boston University, Brown University, MIT Media Lab, The Weizmann Institute of Science, and SRI International.
The team also aims to play a central, coordinating role with other efforts around the country and in Europe to develop similar, privacy-preserving contact-tracing systems.
“This project is being done in true academic style. It’s not a contest; it’s a collective effort on the part of many, many people to get a system working,” Rivest says.