An MIT-led research team has developed a drug capsule that could be used to deliver oral doses of insulin, potentially replacing the injections that people with type 1 diabetes have to give themselves every day.
About the size of a blueberry, the capsule contains a small needle made of compressed insulin, which is injected after the capsule reaches the stomach. In tests in animals, the researchers showed that they could deliver enough insulin to lower blood sugar to levels comparable to those produced by injections given through skin. They also demonstrated that the device can be adapted to deliver other protein drugs.
“We are really hopeful that this new type of capsule could someday help diabetic patients and perhaps anyone who requires therapies that can now only be given by injection or infusion,” says Robert Langer, the David H. Koch Institute Professor, a member of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, and one of the senior authors of the study.
Giovanni Traverso, an assistant professor at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and a visiting scientist in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, where he is starting as a faculty member in 2019, is also a senior author of the study. The first author of the paper, which appears in the Feb. 7 issue of Science, is MIT graduate student Alex Abramson. The research team also includes scientists from the pharmaceutical company Novo Nordisk.
Video credit: Diana Saville
Self-orientation
Several years ago, Traverso, Langer, and their colleagues developed a pill coated with many tiny needles that could be used to inject drugs into the lining of the stomach or the small intestine. For the new capsule, the researchers changed the design to have just one needle, allowing them to avoid injecting drugs into the interior of the stomach, where they would be broken down by stomach acids before having any effect.
The tip of the needle is made of nearly 100 percent compressed, freeze-dried insulin, using the same process used to form tablets of medicine. The shaft of the needle, which does not enter the stomach wall, is made from another biodegradable material.
Within the capsule, the needle is attached to a compressed spring that is held in place by a disk made of sugar. When the capsule is swallowed, water in the stomach dissolves the sugar disk, releasing the spring and injecting the needle into the stomach wall.
The stomach wall has no pain receptors, so the researchers believe that patients would not be able to feel the injection. To ensure that the drug is injected into the stomach wall, the researchers designed their system so that no matter how the capsule lands in the stomach, it can orient itself so the needle is in contact with the lining of the stomach.
“As soon as you take it, you want the system to self-right so that you can ensure contact with the tissue,” Traverso says.
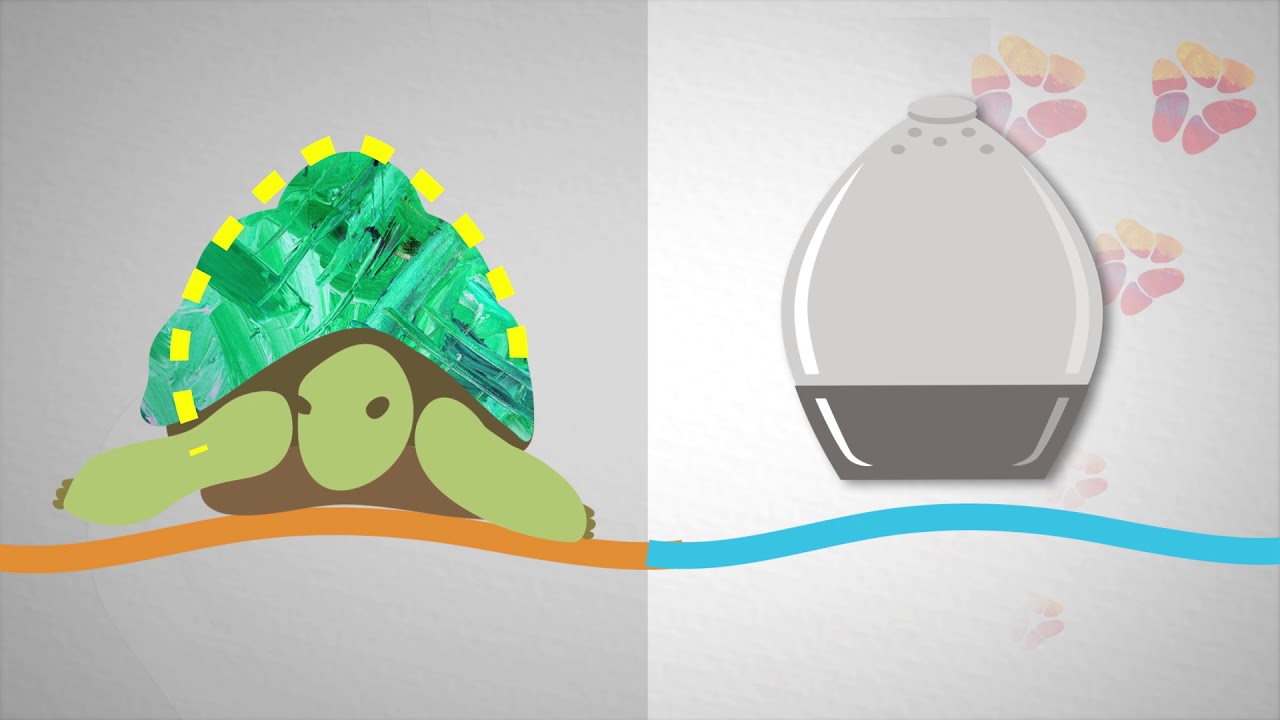
The researchers drew their inspiration for the self-orientation feature from a tortoise known as the leopard tortoise. This tortoise, which is found in Africa, has a shell with a high, steep dome, allowing it to right itself if it rolls onto its back. The researchers used computer modeling to come up with a variant of this shape for their capsule, which allows it to reorient itself even in the dynamic environment of the stomach.
“What’s important is that we have the needle in contact with the tissue when it is injected,” Abramson says. “Also, if a person were to move around or the stomach were to growl, the device would not move from its preferred orientation.”
Once the tip of the needle is injected into the stomach wall, the insulin dissolves at a rate that can be controlled by the researchers as the capsule is prepared. In this study, it took about an hour for all of the insulin to be fully released into the bloodstream.
Easier for patients
In tests in pigs, the researchers showed that they could successfully deliver up to 300 micrograms of insulin. More recently, they have been able to increase the dose to 5 milligrams, which is comparable to the amount that a patient with type 1 diabetes would need to inject.
After the capsule releases its contents, it can pass harmlessly through the digestive system. The researchers found no adverse effects from the capsule, which is made from biodegradable polymer and stainless steel components.
Maria José Alonso, a professor of biopharmaceutics and pharmaceutical technology at the University of Santiago de Compostela in Spain, describes the new capsule as a “radically new technology” that could benefit many patients.
“We are not talking about incremental improvements in insulin absorption, which is what most researchers in the field have done so far. This is by far the most realistic and impactful breakthrough technology disclosed until now for oral peptide delivery,” says Alonso, who was not involved in the research.
The MIT team is now continuing to work with Novo Nordisk to further develop the technology and optimize the manufacturing process for the capsules. They believe this type of drug delivery could be useful for any protein drug that normally has to be injected, such as immunosuppressants used to treat rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. It may also work for nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA.
“Our motivation is to make it easier for patients to take medication, particularly medications that require an injection,” Traverso says. “The classic one is insulin, but there are many others.”
The research was funded by Novo Nordisk, the National Institutes of Health, a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a Viking Olaf Bjork Research Scholarship, and the MIT Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program.
Other authors of the paper include Ester Caffarel-Salvador, Minsoo Khang, David Dellal, David Silverstein, Yuan Gao, Morten Revsgaard Frederiksen, Andreas Vegge, Frantisek Hubalek, Jorrit Water, Anders Friderichsen, Johannes Fels, Rikke Kaae Kirk, Cody Cleveland, Joy Collins, Siddartha Tamang, Alison Hayward, Tomas Landh, Stephen Buckley, Niclas Roxhed, and Ulrik Rahbek.